For the 2024 Image Competition, the ACR sought images with educational or remarkable manifestations representing a diverse range of pediatric patients with autoimmune, inflammatory, infectious and malignant drivers of rheumatic disease. Here, we showcase the winning images from South Asia.
Presentation
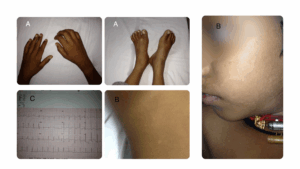
A 9-year-old boy presented with migratory joint pains, swelling, low-grade fever, sore throat and skin rashes. An examination revealed joint tenderness (see Figure A) and erythema marginatum (see Figure B). He had an elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate and high anti-streptolysin O (ASO) titer. An electrocardiogram showed a diffuse T wave inversion (see Figure C) and an echocardiogram showed mild to moderate mitral regurgitation. The diagnosis was confirmed as acute rheumatic fever (ARF) using revised Jones criteria, highlighting carditis and polyarthritis.
The case underscores the importance of early recognition and management of ARF to prevent severe cardiac sequelae and the necessity of secondary prophylaxis to mitigate chronic valvular heart disease risks.
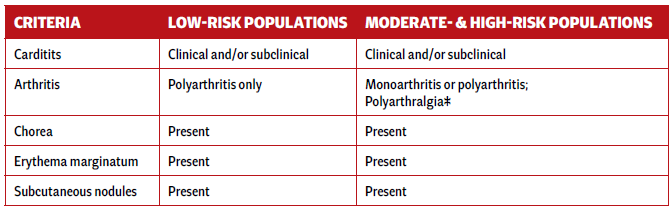
Revised Jones Criteria for the Diagnosis of ARF1
A. Criteria for Diagnosis (with evidence of preceding Group A Streptococcal [GAS] infection)
- Initial ARF—Diagnosis requires:
- 2 major manifestations OR
- 1 major + 2 minor manifestations
- Recurrent ARF—Diagnosis requires:
- 2 major OR
- 1 major + 2 minor OR
- 3 minor manifestations
B. Major Criteria
C. Minor Criteria
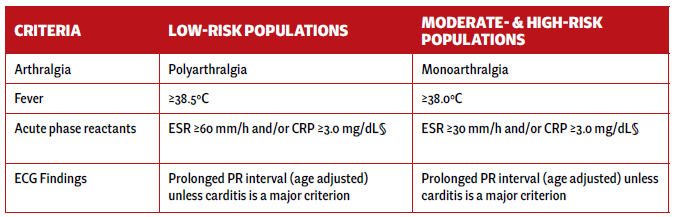
Definitions
Low-risk populations: Incidence of ARF ≤2 per 100,000 school-age children or all-age rheumatic heart disease prevalence ≤1 per 1,000 population/year.
† Carditis: Includes subclinical carditis detected via echocardiography.
‡ Polyarthralgia is a major criterion only in moderate- to high-risk populations after ruling out other causes.
§ CRP must be > upper limit of normal for lab used; ESR may vary over ARF course; peak values should be used.
Evidence of preceding GAS infection (evidence of prior GAS infection may be sought in one of the following ways:
- Positive throat culture for group A beta-hemolytic streptococci;
- Positive rapid streptococcal antigen test; or
- Elevated or rising antistreptococcal antibody titer—either antistreptolysin O (ASO) or antideoxyribonuclease B (ADB).
Sarath Chandra Mouli Veeravalli, MD, FRCP (London), is the clinical director of the Department of Rheumatology, KIMS Hospitals, Secunderabad, Telangana, India.
Reference
- Gewitz MH, Baltimore RS, Tani LY, et al.; American Heart Association Committee on Rheumatic Fever, Endocarditis, and Kawasaki Disease of the Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young. Revision of the Jones Criteria for the diagnosis of acute rheumatic fever in the era of Doppler echocardiography: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2015 May 19;131(20):1806–1818. Erratum in: Circulation. 2020 Jul 28;142(4):e65.
About the Contest
The Rheumatology Image Library is a highly accessed teaching resource, and images from the ACR’s annual contest are added to it, helping keep it dynamic and current. Look for the Best Overall, People’s Choice and regional winners in future issues and on our website.