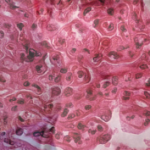
Recent research shows that obinutuzumab—a monoclonal antibody that depletes B cells and is approved for the treatment of B cell malignancies—may benefit patients with lupus nephritis, a condition that can lead to kidney failure.1
The phase 3, randomized controlled Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of Obinutuzumab in Patients with ISN/RPS 2003 Class III or IV Lupus Nephritis (REGENCY) trial in patients with active lupus nephritis showed that obinutuzumab plus standard therapy was more effective than standard therapy alone in achieving a complete renal response in adults with active lupus nephritis.
Almost half of obinutuzumab patients had a complete renal response vs. about one-third of patients who had standard therapy plus placebo.
“These findings really speak to the power of B cell depletion,” says first author Richard Furie, MD, professor at the Feinstein Institutes for Medical Research, Manhasset, N.Y., the Marilyn and Barry Rubenstein Chair in Rheumatology at the Donald and Barbara Zucker School of Medicine at Hofstra/Northwell and chief of the Division of Rheumatology at Northwell Health, Hempstead, N.Y.
B Cell Depletion Drugs
B cells make protective antibodies. But in autoimmune diseases, they make disease-causing antibodies. Dr. Furie noted that early trials of rituximab led to obinutuzumab’s approval for rheumatoid arthritis and vasculitis. Rituximab is a therapeutic monoclonal antibody that binds to a specific protein on B cells and was first approved for the treatment of lymphoma. But early studies of rituximab in systemic lupus, which Dr. Furie calls “the prototypical B cell–driven disease,” and lupus nephritis failed to meet their primary end points.
Further investigation revealed that these trials’ failure to achieve clinical response may have resulted from insufficient B cell depletion as rituximab patients varied in how much they depleted their B cells, Dr. Furie notes. A post-hoc analysis of one of the studies, Lupus Nephritis Assessment with Rituximab (LUNAR), revealed that patients with lupus nephritis who completely depleted B cells had a 3.5-fold higher rate of complete response, compared with those with incomplete B cell depletion.2
Focus on B cell depletion in lupus moved to obinutuzumab, a more potent B cell–depleting antibody. Approved in 2013 for the B cell malignancy chronic lymphocytic leukemia, obinutuzumab outperformed rituximab in head-to-head studies in B cell malignancies, Dr. Furie says. “Since obinutuzumab is a far more potent B cell depleter than rituximab, it made sense to once again study it in lupus nephritis,” Dr. Furie notes.