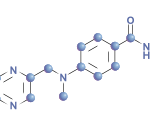
NEW YORK (Reuters Health)—Tofacitinib is better than placebo (and noninferior to etanercept) for treating patients with moderate-to-severe chronic plaque psoriasis, according to Pfizer’s OPT Compare trial.
In an earlier 12-week, phase 2b, dose-ranging trial, the oral JAK inhibitor tofacitinib proved to be more effective than placebo for treating patients with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis.
Based on those encouraging results, Dr. Hervé Bachelez from APHP Hopital Saint-Louis in Paris and colleagues from 122 investigational dermatology centers worldwide compared the efficacy and safety of tofacitinib (5 mg or 10 mg twice daily) with that of etanercept (50 mg subcutaneously twice weekly) or placebo in 1,106 patients with moderate-to-severe chronic plaque psoriasis.
The proportion of patients achieving at least a 75% reduction in Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) score from baseline to week 12 (PASI75) did not differ between tofacitinib 10 mg (63.6%) and etanercept (58.8%), which satisfied the noninferiority criteria.
Tofacitinib 5 mg proved better than placebo (39.5% vs. 5.6%, respectively), but not noninferior to etanercept.
Physician’s Global Assessment responses (which included scores of 0=clear and 1=almost clear) showed a similar pattern: 47.1% of the tofacitinib 5 mg group, 68.2% of the tofacitinib 10 mg group, 66.3% of the etanercept group, and 15.0% of the placebo group.
Similar percentages of the active treatment groups achieved clinically meaningful improvements in Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI) scores at week 12, the researchers report in The Lancet, online June 5.
No more than 4% of patients in any of the groups discontinued treatment because of adverse events.
“This study is the first phase 3 trial of an oral agent (tofacitinib 10 mg twice daily) to show similar efficacy and safety to a biological agent (etanercept) for the treatment of moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis,” the researchers conclude.
“Long-term studies of tofacitinib in plaque psoriasis are ongoing to confirm the efficacy and safety profile beyond the 12-week period assessed in this trial,” they add. “If further results confirm these findings, in the future tofacitinib could provide a convenient and well-tolerated therapeutic option for patients with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis.”
In a related editorial, though, Dr. Mark Lebwohl from Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, questions whether we need more psoriasis therapies, especially in view of the fact that “more than 80% of patients with moderate-to-severe disease are treated only with topical therapy or not at all.”
“The only conclusion one can make from a 12-week study in which fewer than 700 patients were treated with tofacitinib is that the early signals from this trial show a safety profile that is similar to that of etanercept, which is one of the most widely used systemic therapies for psoriasis,” Dr. Lebwohl writes.