CPT codes: 99214-25, 27096, J3301 x1 ICD-9: 720.2, 720.0, 787.02 ICD-10: M46.1*, M45.9*, R11.0 This encounter is coded as 99214 because it includes: Detailed history; Comprehensive examination—eight systems counted; and Medical decision making—moderate complexity (established problem, new problem with no additional workup; new prescription drug ordered). Keep in mind, the CT guidance is an inclusive…
Rheumatology Coding Corner Question: Trigger-Point Injections for Fibromyalgia
A 65-year-old established female patient returns to the office for a follow-up visit for her diagnosis of fibromyalgia. She complains of pain, stiffness and swelling in her left hand, elbow and neck that is persistent since her last visit. The pain is considerably worse in the morning. She denies any fevers, cough or dyspnea. The…
Rheumatology Coding Corner Answer: Trigger Point Injections for Fibromyalgia
Take the challenge. CPT codes: 99213-25, 20553, 73120/LT Diagnosis: ICD-9 7291 ICD-10 M79.7 Coding for trigger-point injections continues to create a lot of confusion on proper coding guidelines. Keep in mind, two CPT4 codes can be used for trigger-point procedures: 20552—Injection(s); single or multiple trigger point(s), one or two muscle(s); and 20553—Single or multiple trigger…

2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting to Offer Coding, Practice Management Sessions
At this year’s ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting in San Francisco, you can take advantage of a variety of sessions designed to address pressing concerns in practice management today. Practice managers, clinicians, office staff and others will enjoy and benefit from hands-on practical sessions and informative panel discussions by top content experts in the field. Here are…

Medicare Incident-to Billing Rules, Pitfalls
In today’s busy rheumatology practices, the services of nurse practitioners, physician assistants, occupational therapists and clinical nurse specialists are a great asset for patient flow, as well as increased revenue. As the growth of nonphysician providers (NPPs) in rheumatology practices has evolved, it has become increasingly important to understand the incident-to rules and avoid the…
Rheumatology Coding Corner Question: Knee Osteoarthritis
Incident-to Billing Case Scenario A 51-year-old female patient returns for a follow-up visit with a physician assistant (PA) for unilateral primary osteoarthritis of her right knee. She had an intraarticular corticosteroid injection of her right knee six weeks prior to her visit. She reports significant improvement in her knee pain and stiffness, and states the…
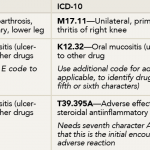
Rheumatology Coding Corner Answer: Knee Osteoarthritis
Diagnoses: ICD-9 715.16, 528.02, E943.8 ICD-10 M17.11, K12.32, T39.395A This was an established patient visit with a new diagnosis. Because the PA sought out the physician to address the new problem and document the assessment and treatment, the visit can still be billed as incident-to. Note: The physician initiated the plan of care for treatment…
Coding Corner Question: April
Coding for an office visit by a patient with osteoarthritis who has a dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) scan
Coding Corner Answer: April
Coding for an office visit by a patient with osteoarthritis who has a dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) scan
Coding Corner Question: March
Coding for chemotherapy infusion with a drug reaction
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- …
- 37
- Next Page »