At this ACR Convergence session, experts provided an overview of the new ACR guideline for juvenile idiopathic arthritis.


At this ACR Convergence session, experts provided an overview of the new ACR guideline for juvenile idiopathic arthritis.

Experts addressed considerations for how to aid patients with juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) in their transition to adult care, specifically highlighting clinical pearls for those with pediatric uveitis and TMJ arthritis.
The early initiation of biologic disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs) may reduce the overall disease burden in patients with polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis (pJIA), according to findings from Ringold et al.
Yalamanchili et al. describe how trends in disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drug (DMARD) use have evolved for insured, U.S. patients with juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Overall, the study found that from 2000 to 2022 in this patient population the use of biologic and targeted synthetic DMARDs rose, while the use of conventional synthetic DMARDs declined.
Noor Alanni, BAO, MB, MBChB |
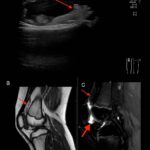
For the 2024 Image Competition, the ACR sought images with educational or remarkable manifestations representing a diverse range of pediatric patients with autoimmune, inflammatory, infectious and malignant drivers of rheumatic disease. Here, we showcase the winning images from the Middle East and North Africa. Lipoma Arborescens Revealed A 10-year-old boy, presented with a five-year history…

The FDA is reviewing supplemental biologics license applications for guselkumab to treat children with juvenile psoriatic arthritis and moderate to severe plaque psoriasis.

Fractures in Patients with SSc By Zsuzsanna McMahan, MD, MHS Why was this study done? To minimize disability due to systemic sclerosis (SSc), it’s important to prevent and manage complications. Many SSc complications and related medications may increase the risk for osteoporosis and fracture. We sought to identify modifiable risk factors for fracture in patients…

Treat to Target in Gout Monitoring & achievement of target serum urate levels By Jing Li & Gabriela Schmajuk, MD, MS Why was this study done? The ACR’s 2020 guideline for the management of gout recommends using a treat-to-target (T2T) approach to lower serum urate (SU). Using the ACR’s RISE registry, we examined the use…
A study from Glerup et al. demonstrated that many patients with juvenile idiopathic arthritis achieved drug-free remission over 18 years of follow-up and that remission rates remained stable between years 8 and 18 of the study period.
Similar patterns of inflammation occur in the joints of patients with inflammatory arthritis, but in each individual, arthritis affects only a subset of possible anatomic areas. Chang et al. set out to identify patient-specific anatomic patterns of joint flare to distinguish local from systemic drivers of chronic disease.