Eaton et al. set out to describe the prevalence, incidence and progression of radiographic and symptomatic hand osteoarthritis (OA), and to evaluate differences according to age, sex, race and other risk factors.
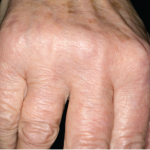

Eaton et al. set out to describe the prevalence, incidence and progression of radiographic and symptomatic hand osteoarthritis (OA), and to evaluate differences according to age, sex, race and other risk factors.
Background & objectives: Patients with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases (RMDs) may be at an increased risk of SARS-CO-V2 infection as a result of underlying disease, associated comorbidities and use of potentially immunosuppressive treatments. Further, concern exists regarding whether individuals with rheumatic diseases potentially experience more severe COVID-19 and poorer outcomes. This study was undertaken to…
Chambers et al. found no evidence of an increased risk of major structural birth defects nor any increase in a wide range of other pregnancy outcomes attributable to prenatal exposure to hydroxychloroquine.
In March A&R, Remaeus et al. reported on the results of their study, which evaluated pregnancy outcomes in relation to anti-rheumatic treatment before and during pregnancy, as a proxy of disease severity in pregnant women with psoriatic arthritis (PsA), compared with those without PsA.

COVID-19 vaccination, treatments for rheumatic disease and more—the Late-Breaking Abstracts session of ACR Convergence 2021 highlighted six studies with implications for rheumatology.
In February A&R, Penso et al. reported on the results of their study, which explored whether patients with psoriasis, PsA and AS have a higher risk of developing IBD when treated with an IL-17 inhibitor compared with apremilast, a phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) inhibitor, or etanercept, a TNF inhibitor.
In January A&R, Simon et al. report a study to assess humoral and cellular immune responses after infection with, or vaccination against, SARS-CoV-2 in patients with B cell depletion and controls who are B cell competent, finding that B cell depletion completely blocks humoral but not T cell SARS-CoV-2 vaccination response. In the same issue, Connolly et al. evaluated disease flare and post-vaccination reactions in patients with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases following messenger RNA (mRNA) vaccination.
A special article in the December issue of Arthritis & Rheumatology summarizes the current understanding of the cardiac toxicity of HCQ and CQ.

A key question many graduating rheumatology fellows face each year is: Are you interested in pursuing a career in academic medicine or in private practice? Although the two tracks are not mutually exclusive, it is true that juggling the demands of scholarly work, medical education and a busy clinical workload is by no means easy….
Gendron et al. undertook this study to investigate the prevalence and prognostic value of conventional and nonconventional antiphospholipid antibodies in patients with COVID-19.