In Situ Adaptive Immunity

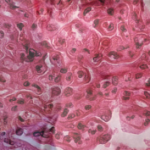
Marcus Clark, MD, chief, Section of Rheumatology, Gwen Knapp Center for Lupus and Immunology Research, the University of Chicago, spoke on in situ adaptive immunity in LN. Among the key points of his talk was the prognostic importance of tubulointerstitial inflammation at the time of biopsy, which is a better indicator than glomerular inflammation in predicting the risk of progression to renal failure, with increased risk of progression to renal failure in patients with moderate to severe tubulointerstitial inflammation.
Severe tubulointerstitial inflammation, he said, is associated with B cell selection in situ mediated by T-follicular helper cells, and the antibodies selected in situ often react with a molecule called vimentin, which is highly expressed in inflammatory infiltrates.
“High-titer serum antibodies to vimentin in the serum appear to be a specific biomarker of severe tubulointerstitial disease,” he said. “This would be the first biomarker in blood for a specific histologic manifestation of LN of such prognostic importance.”
TWEAK

Chaim Putterman, MD, chief, Division of Rheumatology, Albert Einstein College of Medicine and Montefiore Medical Center, Bronx, N.Y., spoke on the TNF-related weak inducer of apoptosis (TWEAK) molecule as a potential therapeutic target and biomarker for active LN. He presented data from a number of studies that show that the TNF-family member cytokine TWEAK, acting through the fibroblast growth factor-inducible 14 (Fn14), promotes inflammatory diseases by activating key cell types that drive pathology locally rather than by modifying adaptive immune responses.
He also highlighted data showing that inhibition of TWEAK signaling is effective in several experimental models of immune-mediated renal disease, including chronic graft-vs.-host (cGVH) disease, nephrotoxic serum nephritis and spontaneous LN in mice (i.e., MRL-lpr/lpr mouse strain).
Data show as well that TWEAK is up-regulated in kidneys of mice and patients with active LN and can be found in the urine of lupus patients with active nephritis. Although he said this does not necessarily mean that TWEAK is pathogenic or directly injurious to the kidney, the presence of TWEAK in the urine of individuals with active LN “suggest a possible role of urinary TWEAK as a biomarker either used alone or maybe as a part of a larger panel of molecules that are up-regulated during nephritis but that wouldn’t be up-regulated in kidneys without active inflammation or in kidneys with nephritis, but not from lupus.”
Based on these and other studies, Dr. Putterman said that a large, multinational, Phase II clinical trial called ATLAS is currently enrolling patients to formally look at the role of an anti-TWEAK antibody as an add-on to the standard of care for patients with LN (see https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01499355?term=ATLAS+and+lupus&rank=1).