He denied any of the following symptoms: sore throat, cough, nasal congestion, hearing loss, chest pain, shortness of breath, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, numbness, tingling, muscle pain or weakness, genital discharge, dysuria and hematuria. The patient reported living with his wife and newborn baby. He denied any use of illicit drugs. He also denied any family history of psoriasis, inflammatory bowel disease, thyroid disease, rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus and other autoimmune disease.
The patient’s physical exam was notable for normal cardiac, pulmonary, abdominal and neurological exams; an erythematous, tender, nodular rash overlying both lower extremities, the mons pubis and lower abdomen (see Figure 1); tenderness without overt synovitis in both elbows; and a warm effusion of his left knee.
Extensive diagnostic testing was performed. Notable findings included normal renal function; elevated alkaline phosphatase at 125 U/L (reference range [RR]: 9–122 U/L) with normal bilirubin, AST and ALT; leukocytosis with 17.9×103 cells/μL white blood cells (WBC; RR: 4.0–11.0×103 cells/μL); and neutrophilia with absolute neutrophil count of 13.24×103 cells/μL (RR: 2.00–7.60×103 cells/μL); mild anemia with hemoglobin of 12.4 g/dL (RR: 13.2–17.1 g/dL); thrombocytosis with platelet count of 498×103 cells/μL (RR: 150–420×103 cells/μL); and elevated, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein of 234.5 mg/L; normal procalcitonin and elevated antistreptolysin O (ASO) titer of 959 IU/mL (RR: ≤200 IU/mL).
Tests were negative for COVID-19, group A Streptococcus, urine chlamydia and gonorrhea, syphilis, QuantiFERON, Lyme antibody, Rickettsia IgG and IgM, hepatitis B surface antigen, hepatitis B total core antibody, hepatitis C antibody and human immunodeficiency virus. Parvovirus DNA was not detected by polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Blood cultures failed to identify a pathogen.
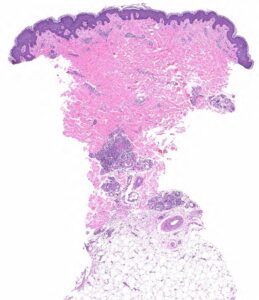
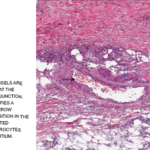
FIGURE 2A: Punch biopsy demonstrates an uninvolved epidermis with focal mid to deep dermal vasculocentric inflammation (H&E stain, 2x). (Click to enlarge.)
Rheumatoid factor was mildly positive at 17 IU/mL (RR: <14 IU/mL); antinuclear antibody (ANA) was 1:80, dense and fine speckled (RR: <1:80); angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) was normal. ANCA, myeloperoxidase antibodies (MPO), proteinase 3 (PR3) and cryoglobulin tests were negative. C3 and C4 were normal. Urinalysis returned 1+ protein and 1+ ketones; urine protein/creatinine was 0.10 mg/1.0 mg (RR: <0.10 mg/1.0 mg). Serum protein electrophoresis was normal, and serum free
kappa/lambda was absent.
Chest X-ray and transthoracic echocardiogram were unrevealing.
Left knee joint aspiration yielded turbid, yellow synovial fluid, with 10,301 nucleated cells/μL (RR: ≥2,000 nucleated cells/μL is classified as inflammatory synovial fluid), less than 3,000 red blood cells and no crystals. Synovial fluid culture did not yield an organism.