As of January 1, physicians can no longer bill the inpatient/outpatient consultation evaluation and management (E/M) codes for Medicare patients. E/M codes for new or established patients should be used as appropriate.
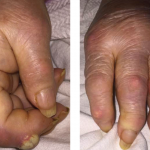
Also, gout codes changed from one ICD-9 code to four codes. This went into effect on October 1, 2009. It is important to add a fifth digit to gout diagnoses in order to be reimbursed.
ad goes here:advert-1
ADVERTISEMENT
SCROLL TO CONTINUE
The gout codes are:
2009 ICD9 Code
ad goes here:advert-2
ADVERTISEMENT
SCROLL TO CONTINUE
- 274.0 Gouty arthropathy
2010 ICD9 Codes (this diagnosis now requires a fifth digit)
- 274.00 Gouty arthropathy, unspecified
- 274.01 Acute gouty arthropathy
- Acute gout
- Gout attack
- Gout flare
- Podagra
- 274.02 Chronic gouty arthropathy without mention of tophus (tophi)
- Chronic gout
- 274.03 Chronic gouty arthropathy with tophus (tophi)
- Chronic tophaceous gout
- Gout with tophi not otherwise specified (NOS)
If you require additional information or assistance with coding or changes for 2010, call the ACR’s coding and reimbursement department at (404) 633-3777 or visit www.rheumatology.org, and click on Practice Support.