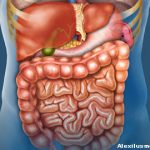
They conclude: “The exact role that anti-TNF therapy plays in improving growth requires further study, including elucidation of more effective treatment strategies to reduce the inflammatory process and promote catch-up growth, so ensuring that young people with IBD can achieve their full growth potential.”
Dr. Cameron did not respond to an interview request by press time.
ad goes here:advert-1
ADVERTISEMENT
SCROLL TO CONTINUE
Reference
- Cameron FL, Altowati MA, Rogers P, et al. Disease status and pubertal stage predict improved growth in anti-TNF therapy for pediatric inflammatory bowel disease. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2016 Sep 21. [Epub ahead of print]