Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and C-reactive protein (CRP) tests performed after the initiation of methylprednisolone were normal. Hepatitis serologies, extractable nuclear antigen (ENA) and ANCA tests were negative. Prior hospital imaging studies were reviewed. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain, performed two years prior when the patient presented to the emergency department with headache and dizziness, showed encephalomalacia and gliosis of the bilateral cerebellum. A CT angiogram of the head and neck was performed to evaluate the cerebral vasculature and demonstrated similar beading involving the carotid and vertebral arteries. The patient also endorsed a history of uterine rupture, which raised suspicion for a collagen vascular disease. Samples were taken for whole exome sequencing and microarray. A purpuric rash of the lower abdomen and a muscle biopsy were performed, but were negative for vasculitis.
The patient’s condition stabilized, and she was quickly tapered off steroids. Whole exome sequencing later revealed a COL3A1 heterozygous variant, c.1241G>T p.Gly414Val, suspected as pathogenic and consistent with vEDS.
Case 2
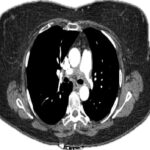
A 52-year-old male with a past medical history of hypertension, hyperlipidemia and prostate cancer (status post-prostatectomy) presented to a hospital with epigastric and left-side abdominal pain. He appeared diaphoretic and pale and had severe abdominal tenderness on examination. His initial blood pressure was 88/46 mmHg. Laboratory studies revealed a hemoglobin of 12g/dL, which represented a 3.8g/dL decrease compared with a recent test performed three days prior to his presentation. A CT of the abdomen and pelvis revealed a large retroperitoneal hemorrhagic mass around the pancreatic tail. Massive transfusion protocol was initiated, and he was transferred to the intensive care unit. A CT angiogram of the abdomen showed an enlarging retroperitoneal hematoma with active bleeding. Multifocal narrowing of the celiac and inferior mesenteric arteries was noted, with areas of occlusion. There was focal dissection of the celiac artery and thrombotic occlusion of the proximal inferior mesenteric artery. The pattern of arterial involvement was considered consistent with vasculitis.
The patient remained hypotensive despite fluid resuscitation and vasopressor support and later became obtunded. He was intubated and shortly afterward went into cardiac arrest. Advanced cardiovascular life support was performed with return of spontaneous circulation achieved after five minutes. A mesenteric angiogram was performed by interventional radiology. Active extravasation was found from a branch of the inferior pancreaticoduodenal artery, which was successfully embolized. Ectasias and aneurysms from multiple superior mesenteric artery (SMA) branches, as well as multiple visceral aneurysms, were noted, along with similar findings in the bilateral renal and celiac arteries.