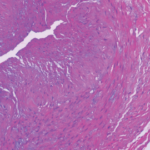
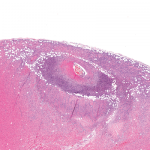
Not Every Inflamed Temporal Artery Is Due to GCA
An important section of our consensus document speaks to the differential diagnosis of active arteritis in a temporal artery biopsy. We acknowledge that most such cases will represent GCA, especially in the context of high clinical suspicion (pre-test probability) and the marked prevalence of GCA compared with the other conditions, especially in the temporal artery. That said, especially for unusual presentations of disease, the consideration of other diagnoses remains valuable.
Synoptic Reporting & Scoring?
Our consensus presents recommended report formats but stops short of an overly synoptic report. The use of such reporting templates is prevalent in cancer diagnostics, but is not yet mature in non-neoplastic diagnoses. We know that every patient has a unique case of the disease, and as much as we lump these into GCA, personalized medicine dictates we go deeper. A uniform terminology sets the groundwork for developing such synoptic reports, and those may inform multi-modality diagnostic criteria, scoring of disease, choice of therapeutic approach, enrollment in clinical trials and evolution of future guidelines from our respective societies—or even combined guidelines.
We Need to Work Together
Please involve pathologists in your multidisciplinary discussions for GCA and any other tissue-based diagnosis. Communication and partnership are key to evolving understanding in these diseases.
Moayad Alqazlan, MBBS, is a cardiovascular pathology fellow in the Department of Laboratory Medicine and Pathobiology, University of Toronto, Ontario.
Vidhya Nair, MBBS, MD, is chair of the Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, University of Ottawa, Ontario.
Michael A. Seidman, MD, PhD, is director of quality and safety in surgical pathology, director of autopsy, and staff pathologist at the University Health Network Laboratory Medicine Program at Toronto General Hospital. He is an assistant professor in the Department of Laboratory Medicine and Pathobiology, University of Toronto, Ontario.
References
- Nair V, Fishbein GA, Padera R, et al. Consensus statement on the processing, interpretation and reporting of temporal artery biopsy for arteritis. Cardiovasc Pathol. 2023 Nov–Dec;67:107574.
- Maz M, Chung SA, Abril A, et al. 2021 American College of Rheumatology/Vasculitis Foundation Guideline for the management of giant cell arteritis and Takayasu arteritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021 Aug;73(8):1349–1365.
- Ponte C, Grayson PC, Robson JC, et al. 2022 American College of Rheumatology/EULAR classification criteria for giant cell arteritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022 Dec;74(12):1881–1889.
- Rubenstein E, Maldini C, Gonzalez-Chiappe S, Chevret S, Mahr A. Sensitivity of temporal artery biopsy in the diagnosis of giant cell arteritis: A systematic literature review and meta-analysis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2020 May 1;59(5):1011–1020.
- Dua AB, Husainat NM, Kalot MA, et al. Giant cell arteritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of test accuracy and benefits and harms of common treatments. ACR Open Rheumatol. 2021 Jul;3(7):429–441.