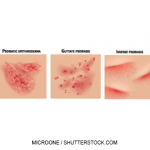
 In early February, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved a single-dose, single-press autoinjector for guselkumab, an interleukin 23 blocker indicated for the treatment of adults with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis who are candidates for systemic or phototherapy.1 The injector fits comfortably in a patient’s hand and provides a controlled autoinjection with a hidden needle. The agency initially approved guselkumab on July 13, 2017.2
In early February, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved a single-dose, single-press autoinjector for guselkumab, an interleukin 23 blocker indicated for the treatment of adults with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis who are candidates for systemic or phototherapy.1 The injector fits comfortably in a patient’s hand and provides a controlled autoinjection with a hidden needle. The agency initially approved guselkumab on July 13, 2017.2
The single-press injection device, Tremfya, administers a 100 mg subcutaneous dose of guselkumab. It can be used once every eight weeks, after a patient receives the initial guselkumab doses at Weeks 0 and 4. The injector is intended for use under direct supervision and guidance of a physician. Once trained and approved by their physician, patients may self-inject. A soft click can be heard when the drug administration is complete, and a safety system protects patient from an accidental needlestick after use.
A validated, self-injection assessment questionnaire was administered during the phase 3 multicenter, randomized ORION trial. The questionnaire evaluated the patient experience at Weeks 0, 4 and 12, rating usage on a scale of 0 (worst) to 10 (best) across six domains: feelings about self-injection, self-image, self-confidence, pain and skin reaction during or after the injection, ease of use of the self-injection device and self-injection satisfaction. The mean score for satisfaction was 9.18 for self-injection and 9.24 for ease of use. After three injections, patients continued to report favorable scores for the device’s usability.
The safety and efficacy of the Tremfya injection device was also evaluated in the ORION trial. Guselkumab-treated patients had a significantly greater response than placebo-treated patients for PASI 90, PASI 100 and Investigator’s Global Assessment scores. The majority of injection-site reactions were mild and transient.
Michele B. Kaufman, PharmD, BCGP, is a freelance medical writer based in New York City and a pharmacist at New York Presbyterian Lower Manhattan Hospital.
References
- Janssen Global Services LLC. News release: Janssen announces U.S. FDA approval of novel Tremfya (guselkumab) one-press, patient-controlled injector for adults with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis. 2019 Feb 27.
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Biologics application approval letter: Guselkumab. 2017 Jul 13.