The patient reported initial improvement in his weakness, but his CPK remained elevated (although lower than his admission levels). On day six of his hospitalization, he reported worsening weakness with dyspnea on exertion and at rest. He underwent an NIF and CT angiogram (CTA) of his chest for evaluation of new onset respiratory distress. His NIF was low (-5), and his repeat chest CTA highlighted atelectasis without any consolidations or effusions or embolism. We intubated him for poor inspiratory effort, and gave him pulse-dose steroids for three days. We added intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) because the patient had severe respiratory muscle involvement leading to respiratory failure, along with profound muscle weakness despite the initial steroid therapy.
On day eight of his hospitalization, he developed severe pneumococcal sepsis with distributive shock, requiring four vasopressors. His family decided to withdraw care after discussion with the intensive care team and pulmonologist.
Unlike other statin-associated myopathies, HMGCR Ab-related IMNM features a complex pathogenesis characterized by extensive myocyte necrosis with scarce phlogistic infiltration in biopsy & the presence of HMGCR antibodies.
Case Report 2
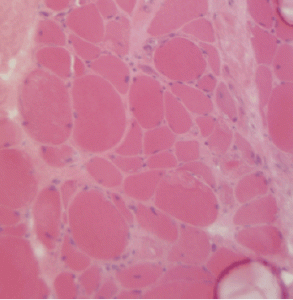
Figure 2A: This H&E stain of Patient 2’s muscle biopsy shows necrotic muscle fibers with mild inflammatory cell infiltration.
The second patient was a 47-year-old African-American male with a progressive subacute proximal weakness of his upper and lower extremities. His symptoms started eight weeks prior to admission and gradually worsened. The patient also reported having difficulty swallowing, nasal regurgitation, dyspnea on exertion and voice changes. These symptoms also started eight weeks prior to hospitalization.
His review of systems was negative for diplopia, skin rash, B type symptoms, cough and joint pain. His past medical history was significant for hypertension, stroke with right-side residual weakness, and hypercholesterolemia. At home, the patient was taking rosuvastatin, lisinopril and aspirin without any recent change in the doses.
On physical examination, we noticed tachypnea, shallow breathing, profound proximal muscle weakness, a weak cough and a low-pitched, husky voice. The rest of his physical examination proved unremarkable.
His initial laboratory work-up revealed mild normocytic normochromic anemia (hemoglobin 11.2 g/dL), normal creatinine (1.0 mg/dL), elevated AST levels (323 IU/L) and significantly elevated CPK levels (10,214 U/L). We grew concerned about statin-induced myopathy, so we discontinued rosuvastatin. His ancillary test revealed negative ANA and a positive extended myositis panel with HMGCR Ab >200 U. His EMG was consistent with irritable myopathy. The patient underwent a muscle biopsy from his right deltoid muscle, which revealed atrophic and necrotic muscle fibers, and mild inflammatory infiltrate.