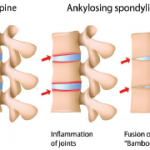
Dr. McGonagle then addressed one of the major therapeutic paradoxes in the field: why do IL-23 inhibitors work in psoriasis and peripheral arthritis, but fail in axial disease? The axial skeleton is enriched in neutrophils and type 17 T cells due to local myelopoiesis, meaning there is greater IL-23 production, as well as IL-17 production independent of neutrophil derived IL-23. Studies have demonstrated a relative paucity of Type 17 T cells at entheses, meaning that IL-17 production is IL-23 dependent, and thus can be halted by IL-23 inhibition alone.7 Variations in the cell types of these tissue compartments may explain the inefficacy of IL-23 inhibitors or the potential need for higher dose IL-23 inhibition in axial disease.1
In summary, neutrophils play a central role in spondyloarthritis and enthesis immunity. Their interactions with IL-23 provide a mechanistic explanation for enthesitis, skin and gut inflammation, and the failure of IL-23 inhibition in axial disease. Dr. McGonagle’s research demonstrates the importance of understanding neutrophil function to guide precise therapeutic strategies in spondyloarthritis.
The HIF-MIF Axis in a Murine Spondylarthritis Model
Dr. Haroon shifted gears to detailing the MIF-HIX axis and the role of neutrophils in the pathogenesis of spondyloarthritis using a pre-clinical spondyloarthritis murine model.
The interest in MIF, also known as macrophage inhibitory factor, came about after the report of anti-CD74 antibodies in axial spondyloarthritis. CD74 is a surface receptor for MIF, which is a protein involved in innate immunity. Under normal circumstances, MIF binds to CD74, leading to inflammation and bone proliferation: both cardinal features of spondyloarthritis.
Dr. Haroon began by examining the serum of patients with axial spondyloarthritis and found elevated levels of MIF, which was also found to be an independent risk factor for disease progression.8 In the tissues, MIF was found in increased levels in Paneth cells in the gut. Likewise, there was greater MIF expression in spinal tissues in patients with axial spondyloarthritis relative to those with osteoarthritis.
With the pro-inflammatory effect of MIF in mind, they found that treatment of healthy peripheral blood monocytes with MIF led to greater TNF alpha production. Likewise, blocking intracellular disassociation of CD74, TNF alpha production was halted. They then took SaOS22 cell lines, induced them with MIF, and found greater osteoblastic activity.
Dr. Haroon then introduced the SKG mouse model, which was the basis for the remainder of his presentation. Curdlan-treated SKG mice develop a spondyloarthritis-like phenotype with weight loss, arthritis, dermatitis and blepharitis. In these mice, they demonstrated increased expression of MIF and its receptor CD74. Even in the ankle joint synovium, as well as in the sacroiliac joint, there was increased MIF and CD74 expression.10