 Baricitinib (Olumiant) is a Janus kinase inhibitor designed to treat moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in patients who have not responded to standard therapies. New research released at the Annual European Congress of Rheumatology (EULAR 2017) in Madrid provides insight into the treatment’s efficacy.
Baricitinib (Olumiant) is a Janus kinase inhibitor designed to treat moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in patients who have not responded to standard therapies. New research released at the Annual European Congress of Rheumatology (EULAR 2017) in Madrid provides insight into the treatment’s efficacy.
In other news, baricitinib has been approved for use in Japan and was recommended as an RA treatment by the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) in the U.K.
New Research
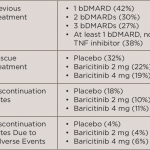
Released at EULAR 2017, a new analysis of data from eight clinical trials found that baricitinib– and placebo-treated patients with moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis (RA) had similar incidence rates of serious infections. Additionally, data from Phase 3 long-term extension trials showed that after two years of baricitinib treatment, patients experienced a significantly lower rate of joint damage progression and continued to have low disease activity throughout treatment. These results were presented during an oral presentation and at two poster presentations.1
During the long-term extension trials, achieving a Simplified Disease Activity Index (SDAI) score of or less than 11 was considered low disease activity. Specifically in one trial, the progression of structural joint damage measured by change in the van der Heijde modified total Sharp score was significantly lower in baricitinib-treated patients throughout the two-year period compared with patients treated with placebo or methotrexate before switching to baricitinib.
Additionally, the long-term extension studies showed that among patients treated with baricitinib for up to three years, the proportion of patients with low disease activity at Week 24 in different treatment groups across the trials remained similar or increased after three years. Most patients who were responsive to baricitinib before entering a long-term extension study maintained their response throughout the study.
Approvals
In July, baricitinib received approval from Japan’s Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare to treat RA in patients who have an inadequate response to standard therapies.2 This approval was based on a review of data from four late-stage clinical trials with more than 3,000 patients with moderate to severe RA worldwide, including more than 500 Japanese patients. In Japan, it is estimated that approximately 700,000–800,000 patients suffer from RA.
The treatment was also recently deemed cost effective by NICE in the U.K. and was recommended to the National Health Services (NHS) as a treatment for patients with severe active RA who have not responded to intensive therapy with conventional disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs.3 The NICE approval was based on data from Phase 3 trials showing that baricitinib-treated patients had significant improvement in the ACR20 response compared with placebo-treated patients. Baricitinib-treated patients also showed promise in preventing progressive radiographic structural joint damage compared with placebo-treated patients, through Week 52 of treatment. Baricitinib-treated patients also had better ACR20 responses compared with methotrexate-treated patients.