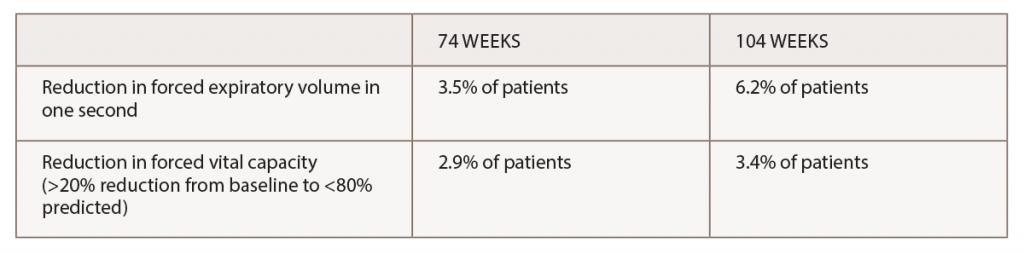
(click for larger image) Table 2. Pulmonary Function*
*Most pulmonary changes were transient and infrequently associated with adverse events.
Dr. Burmester also highlights the sustained efficacy found when combining the trial data. “We observed clinically meaningful, long-term efficacy in patients receiving mavrilimumab for up to more than three years across many disease activity parameters.”
The study found that efficacy was sustained, with 65% of patients achieving a DAS28-CRP of <3.2 and 40.6% of patients achieving DAS28-CRP of <2.6.

Prof. Hamilton
Commenting on the study, Professor John Hamilton, PhD, DSc, Department of Medicine, University of Melbourne, The Royal Melbourne Hospital, Parkville, Victoria, Australia, underscores the safety results and sustained benefits found in the study. “There were no serious adverse events following a unique and detailed analysis, particularly of pulmonary function,” he says. “Long-term treatment was associated with clear and sustained benefits in measures of RA disease which were similar to those reported in early phase 2 studies.”
An important finding verified in the study was that a higher dose of mavrilimumab is needed given the findings of the phase 2 1071 study, in which 150 mg conferred the greatest benefit.2 “It is recommended that phase 3 studies be undertaken using a higher dose,” says Professor Hamilton.
Biomarkers
Along with assessing safety and long-term efficacy outcomes of these three trials, Dr. Burmester and colleagues analyzed biomarkers related to the GM-CSF pathway to better understand the mechanisms of action of mavrilimumab. As in previous studies, this study found and confirmed two biomarkers specifically related to the GM-CSF pathway: CCL17/TARC and CCL22/MDC.1-3
“These biomarkers indicate a potential benefit of inhibiting this pathway in RA treatment,” says Dr. Burmester.
Professor Hamilton agrees. He says the identified biomarkers “may be useful” when designing and implementing future phase 3 trials of mavrilimumab.
Mary Beth Nierengarten is a freelance medical journalist based in Minneapolis.
References
- Burmester GR, McInnes IB, Kremer JM, et al. Mavrilimumab, a fully human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor receptor α monoclonal antibody: Long-term safety and efficacy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018 May;70(5):679–689.
- Burmester GR, McInnes IB, Kremer J, et al. A randomised phase IIb study of mavrilimumab, a novel GM-CSF receptor a monoclonal antibody, in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017 Jun;76(6):1020–1030.
- Weinblatt M, McInnes I, Kremer J, et al. EARTHEXPLORER 2, a phase IIb exploratory study evaluating efficacy and safety of mavrilimumab, a fully human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor receptor-α monoclonal antibody, and the tumor necrosis factor antagonist golimumab in rheumatoid arthritis [abstract 1619]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016;68(suppl 10).
- Burmester GR, McInnes IB, Kremer JM, et al. Mavrilimumab, a fully human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor receptor-α monoclonal antibody: Long-term safety and efficacy for up to 158 weeks of treatment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis [abstract 1616]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016;68(suppl 10).