CARDIOVASCULAR
RUTH Trial Urges Caution when Prescribing Raloxifene
By Robyn T. Domsic, MD
Barrett-Connor E, Mosca L, Collins P, et al. for the Raloxifene Use for The Heart (RUTH) Trial Investigators. Effects of Raloxifene on Cardiovascular Events and Breast Cancer in Postmenopausal Women. NEJM. 2006;355:125-137.
Abstract
Background: The effect of raloxifene, a selective estrogen-receptor modulator, on coronary heart disease (CHD) and breast cancer is not established.
Methods: We randomly assigned 10,101 postmenopausal women (mean age, 67.5) with CHD or multiple risk factors for CHD to 60 mg of raloxifene daily or placebo and followed them for a median of 5.6 years. The two primary outcomes were coronary events (i.e., death from coronary causes, myocardial infarction, or hospitalization for an acute coronary syndrome) and invasive breast cancer.
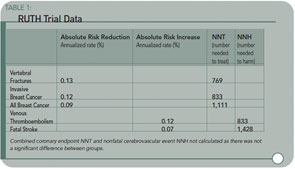
Results: As compared with placebo, raloxifene had no significant effect on the risk of primary coronary events (533 versus 553 events; hazard ratio, 0.95; 95% confidence interval, 0.84 to 1.07), and it reduced the risk of invasive breast cancer (40 versus 70 events; hazard ratio, 0.56; 95% confidence interval, 0.38 to 0.83; absolute risk reduction, 1.2 invasive breast cancers per 1000 women treated for one year); the benefit was primarily due to a reduced risk of estrogen receptor–positive invasive breast cancers. There was no significant difference in the rates of death from any cause or total stroke according to group assignment, but raloxifene was associated with an increased risk of fatal stroke (59 versus 39 events; hazard ratio, 1.49; 95% confidence interval, 1.00 to 2.24; absolute risk increase, 0.7 per 1,000 woman-years) and venous thromboembolism (103 versus 71 events; hazard ratio, 1.44; 95% confidence interval, 1.06 to 1.95; absolute risk increase, 1.2 per 1,000 woman-years). Raloxifene reduced the risk of clinical vertebral fractures (64 versus 97 events; hazard ratio, 0.65; 95 % confidence interval, 0.47 to 0.89; absolute risk reduction, 1.3 per 1000).
Conclusions: Raloxifene did not significantly affect the risk of CHD. The benefits of raloxifene in reducing the risks of invasive breast cancer and vertebral fracture should be weighed against the increased risks of venous thromboembolism and fatal stroke.
Commentary
The role of raloxifene in the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis has been in a state of flux because concerns about hormonal therapy arose with the Women’s Health Initiative trial. In patients unable to take a bisphosphonate, or in those who were merely osteopenic, raloxifene has nevertheless remained a treatment option. As we can recall, the MORE (Multiple Outcomes of Raloxifene Evaluation) trial, published in 1999, suggested a 30% relative risk reduction in vertebral fractures among women with osteoporosis treated for three years, and reported an increase in femoral neck and spine density with raloxifene.1 This drug was then approved for use in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis by the Food and Drug Administration.