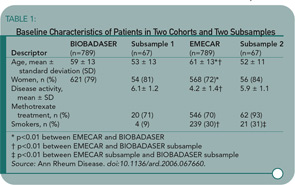
These methodologic issues were apparent to the investigators, but is it unclear how completely this potential source of bias was managed in their analyses. Recognizing potential differences in the two cohorts, the investigators created two propensity-matched cohorts. They matched patients on their probability of receiving a TNF antagonist. These sub-samples are better matched than the parent cohorts on age, gender, and Disease Activity Score, but they are not well matched with respect to methotrexate use and smoking habit (see Table 1, above right). Moreover, the percentage of patients and sample sizes suggest that many patients have missing data (see methotrexate for an example). The propensity score method can be quite useful when it produces comparison groups well balanced on relevant confounders; however, Table 1 demonstrates that the matched subsamples are not adequately balanced.
The authors then compare the samples from the parent cohort to calculate rate ratios. They note a significantly reduced all-cause mortality-rate ratio for the TNF antagonists compared with synthetic-DMARD users. However, based on the imbalances in the parent cohort, these comparisons are of limited value. The unadjusted rate ratios from the propensity-matched cohorts are also of limited value because of the recognized differences in smoking habits. Moreover, the lack of information on many other potentially important covariates makes it impossible to evaluate the validity of any of their comparisons.
This paper is valuable in stating that there is no increase in mortality associated with TNF antagonists. However, statements about a reduction in mortality are not clearly supported by their data. Valid comparisons can only be made between groups that overlap in their characteristics, thus allowing for adjustment in regression analyses. While registries will enhance our understanding of the safety and effectiveness of RA treatments, we have not yet established valid methods for studying registries.
Catalogue the Complexity of RA Care
By Michael M. Ward, MD
Kahn KL, MacLean CH, Liu H, et al. The complexity of care for patients with rheumatoid arthritis: metrics for better understanding chronic disease care. Med Care. 2007;45(1):55-65.
Abstract
Background: Patients with RA provide an important opportunity for understanding care of patients with a serious chronic condition.
Objective: We sought to characterize the complexity of care for patients with RA, including metrics describing the patient, the disease, and use of the healthcare system across time and place.
Methods: We undertook a prospective cohort study of 568 community-dwelling patients with RA by using observational data from clinically detailed telephone interviews at baseline and two years later in addition to medical record abstraction. Health status, comorbidity, use of DMARDs, visits, providers, provider types, encounter settings, and the discontinuity between patients and providers were studied.