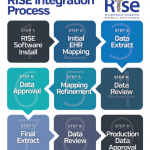
In 2014, the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) launched the Rheumatology Informatics System for Effectiveness (RISE), a national electronic health record (EHR)–enabled registry that passively collects data from the EHR programs of participating practices. The system is federally certified through the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) as a Qualified Clinical Data Registry (QCDR), allowing collection of data without individual patient-informed consent.
“RISE aims to decrease the burden of data collection on practices, to streamline participation in federal quality programs and to facilitate local rapid-cycle quality improvement by providing continuous performance feedback and benchmarking,” write Jinoos Yazdany, MD, MPH, of the University of California, San Francisco, and her colleagues in their latest analysis, published in the December 2016 issue of Arthritis Care & Research.
Dr. Yazdany and colleagues reported on RISE’s structure and analyzed data from the registry captured between Oct. 1, 2014, and Sept. 30, 2015, to characterize initial practices, patient data and medication use among patients diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). They also reported the initial results of quality measures collected by the system, such as disease activity scores.
The Structure
All data automatically collected by RISE are transferred to a central data warehouse. The system is compatible with 30 different EHR programs and eliminates data entry for practices. Participating practices have access to RISE data through an online dashboard where they can view national benchmarks for quality measures, and practice- and clinician-level performance. They can also run customized queries on their own patient population and perform basic data analyses.
RISE’s privacy and security framework are HIPAA compliant, and its research procedures were approved by the Western Institutional Review Board. Because data collected through QCDR systems are designed to improve quality, there is a waiver of individual patient informed consent for registry data capture. All RISE data used for research, as well as aggregate Medicare data requested by CMS, can be de-identified, meaning protected health information is masked. Research requests undergo a formal committee review through the ACR. And “any identified data, including text from clinical notes, will remain within the clinical data warehouse and will be analyzed centrally,” note the authors.
The Stats
From Oct. 1, 2014, to Sept. 30, 2015, the registry collected data from 55 participating sites and 312 clinicians on 239,302 patients. Of the participating sites, 72% are in group practice, 21% in solo practice and 7% are part of a larger health system.