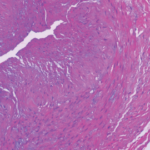
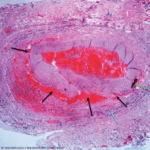
In summary, ultrasound is becoming an increasingly important and highly practical tool for the diagnosis of GCA; however, its implementation is limited by a requirement for technical expertise in performing and interpreting the scans. Likewise, due to the risk of false positive ultrasounds and cases of intermediate pre-test probability, biopsy and other imaging modalities remain important tools in the rheumatologist’s diagnostic armamentarium.
Michael Cammarata, MD, RhMSUS, is an assistant professor of medicine at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore.
ad goes here:advert-1
ADVERTISEMENT
SCROLL TO CONTINUE
References
- Maz M, Chung SA, Abril A, et al. 2021 American College of Rheumatology/Vasculitis Foundation Guideline for the Management of Giant Cell Arteritis and Takayasu Arteritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021 Aug;73(8):1349–1365.
- Dejaco C, Ramiro S, Bond M, et al. EULAR recommendations for the use of imaging in large vessel vasculitis in clinical practice: 2023 update. Ann Rheum Dis. 2024 May 15;83(6):741–751.
- Ponte C, Grayson PC, Robson JC, et al. 2022 American College of Rheumatology/EULAR classification criteria for giant cell arteritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2022 Dec;81(12):1647–1653.
- Bowling K, Rait J, Atkinson J, Srinivas G. Temporal artery biopsy in the diagnosis of giant cell arteritis: Does the end justify the means? Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2017 Jun 15;20:1–5.
- Schmidt WA, Kraft HE, Vorpahl K, Völker L, Gromnica-Ihle EJ. Color duplex ultrasonography in the diagnosis of temporal arteritis. N Engl J Med. 1997 Nov 6;337(19):1336–1342.
- Schmidt WA. Vascular ultrasound in rheumatology practice. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2023 Mar;37(1):101847.
- Molina-Collada J, Castrejón I, Rivera J, et al. The role of ultrasound and FDG-PET/CT to detect extracranial artery involvement in patients with suspected large vessel vasculitis. Mod Rheumatol. 2023 Apr 13;33(3):549–556.
- Dejaco C, Ponte C, Monti S, et al. The provisional OMERACT ultrasonography score for giant cell arteritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2023 Apr;82(4):556–564.
- Monti S, Ponte C, Schäfer VS, et al. The giant cell arteritis (GCA) ultrasound score (OGUS) at diagnosis and after initial treatment predicts future relapses in GCA patients: Results of a multicentre prospective study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2025 May;84(5):823–832.
- Patil P, Williams M, Maw WW, et al. Fast track pathway reduces sight loss in giant cell arteritis: results of a longitudinal observational cohort study. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2015 Mar–Apr;33(2 Suppl 89):S103–S106.
- Schmidt WA, Czihal M, Gernert M, et al. Recommendations for defining giant cell arteritis fast-track clinics. English version. Empfehlungen zur Definition von Riesenzellarteriitis-Fast-Track-Kliniken. Z Rheumatol. 2024 Dec;83(Suppl 3):285–288.
- Mackie SL, Dejaco C, Appenzeller S, et al. British Society for Rheumatology guideline on diagnosis and treatment of giant cell arteritis: executive summary. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2020 Mar 1;59(3):487–494.
- Schmidt WA, Schäfer VS. Diagnosing vasculitis with ultrasound: Findings and pitfalls. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2024 Jun 5;16:1759720X241251742.