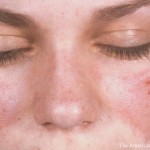
In a recent review, researchers addressed skin injury in patients with SLE, discussing the effects of ultraviolet rays on the skin and the subsequent generation of autoantibodies. They concluded that UV rays activate immune cells where IgG has been deposited, resulting in inflammation…