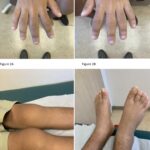
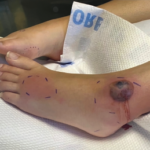
Pachydermoperiostosis (PDP), also known as Touraine-Solente-Golé syndrome or primary hypertrophic osteoarthropathy, is a rare syndrome that can be inherited as autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive, or sporadically. This progressive disease primarily affects males, who tend to have more severe features than females. PDP usually occurs during adolescence, often starting around puberty.1 The main clinical features are…