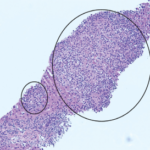
In Patient 1, we noted improvement in symptoms of ECD, as well as clear radiological improvement over a four-month course of using 8 mg/kg tocilizumab IV every four weeks.
In Patient 2, we noted clinical stabilization and some early radiographic improvement.
Known risks of TCZ include immunosuppression, elevated LFTs, cytopenias, elevated cholesterol and, rarely, bowel perforation.18 The most notable side effect in our patients was recurrent urinary tract infections in our second case, which may have been related to the medication or the underlying disease process.
Our clinical results are limited by the small sample size of two patients. The two patients described did not have CNS involvement, which is an independent predictor of death. Also, we did not obtain cardiac imaging in our patients to screen for preclinical cardiac involvement. Advances in cardiac imaging suggest that cardiac involvement may be more common than once thought in ECD, and experts now recommend screening for occult cardiac involvement.16,19
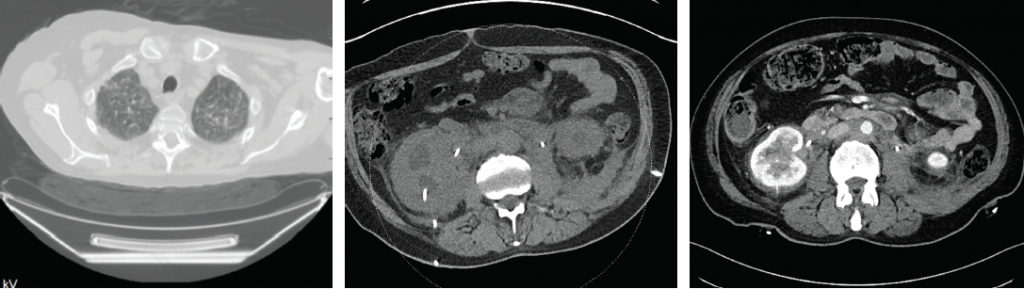
Figures 4A–C demonstrate the response to treatment in Patients 1 and 2. 4A is the CT scan of Patient 1 and demonstrates resolution of the ground-glass opacities in the lungs after treatment. 4B and 4C are the abdominal CT scans of Patient 2 before (4B) and after (4C) treatment.
What Lies Ahead
A prospective, open-label, single-arm, Phase 2, pilot study of tocilizumab in patients with ECD is ongoing. Recruitment began in 2012; unfortunately, recruitment into meaningful prospective trials is made difficult by the rarity of the disease.
In our cases, we show dramatic improvement with anti-IL-6 therapy and think it warrants more study. Current therapy is suboptimal, and there is a role for alternative treatments in ECD.
Stefanie D. Wade, MD, is completing her internal medicine residency at the University of Connecticut Health Center and plans to pursue a fellowship in rheumatology.
Michael A. Seidman, MD, is a pathologist and researcher at St. Paul’s Hospital in downtown Vancouver, Canada.
Edward C. Jones, MD, is a consultant anatomical pathologist at the Vancouver General Hospital and a clinical professor at the University of British Columbia.
Arnold Radu, MD, completed his radiology residency at McGill University and has finished a musculoskeletal fellowship at Vancouver General Hospital.
Ryan Paterson, MD, is an assistant professor in the Department of Urologic Sciences at Vancouver Hospital and Providence Health Care. He graduated UBC for medical school and was an Endourology and Laparoscopy, American Foundation for Urologic Disease Scholar.