Pressmaster/shutterstock.com
WASHINGTON, D.C.—The importance of biomedical research to advancing clinical care with the ultimate goal of improving patients’ lives was on display during an ACR Discovery 2016 plenary session at the 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting.
The session offered new ways to think about and treat select rheumatologic diseases, including research showing for the first time the efficacy of a steroid-sparing medication for giant cell arteritis (GCA), research suggesting that statins may lower mortality risk in patients with ankylosing spondylitis (AS) or psoriatic arthritis (PsA) and research showing the importance of normalizing uric acid levels to improve renal function in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD).
Steroid-Sparing Medication for GCA
“The era of unending glucocorticoid treatment with no viable alternative is over,” said John H. Stone, MD, MPH, director of clinical rheumatology and the Edward A. Fox Chair in Medicine at the Massachusetts General Hospital, who presented the findings of the GiACTA trial.
The GiACTA trial, the largest trial ever conducted of patients with GCA, enrolled 251 patients from 14 countries and 76 sites for 22 months to evaluate the efficacy and safety of tocilizumab for patients with GCA. Dr. Stone said that GiACTA is also the first trial for any disease to employ a blinded, variable-dose, steroid-tapering regimen.
The trial compared the efficacy of four different treatment arms for patients with GCA: 26-week prednisone taper (PBO + 26; n=50), 52-week prednisone taper (PBO + 52; n=50), tocilizumab 162 mg once weekly + PBO + 26 (TCZ QW; n=100), and tocilizumab 162 mg once every two weeks + PBO + 26 (TCZ Q2W; n=50).
At 52 weeks, the study showed significantly greater sustained remission in patients treated with tocilizumab compared with prednisone (see Table ).
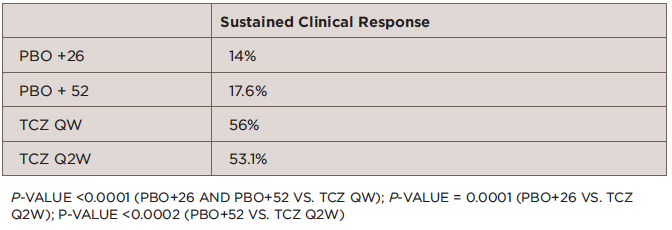
TABLE 1: Primary Outcome: Sustained Remission from Week 12 to Week 52
The most surprising finding of the study, according to Dr. Stone, was the poor results in the patients treated with prednisone only. “I think most rheumatologists will find it surprising that the therapy we have regarded as the standard of care—that has been the standard of care for many decades—fared so poorly,” he said.
Along with the significant benefit to adding tocilizumab, the study found no significant differences in adverse events among the treatment arms. “In fact, patients in the steroid-only groups were more likely to experience more than one serious adverse event than were those in the tocilizumab groups,” he said, adding that this “underscores the major contribution of glucocorticoids to toxicity in this disease.”