The medical decision making (MDM) of an evaluation and management visit is just one part of a patient’s visit. Rheumatologists can make the mistake of thinking that the level of visit can be determined just by the MDM, but that is often not the case.
MDM comprises three elements:
- Complexity of determining diagnoses or management options;
- Amount and/or complexity of data that needs to be reviewed; and
- Risk of complications and/or morbidity or mortality.
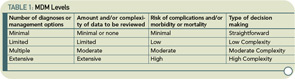
Also, there are four levels of MDM: minimal, limited, multiple, and extensive. To qualify for a level of MDM, two of the three elements in Table 1 (above right) must be met.
Number of Diagnoses or Management Options
This element is based on the number and types of problems and the complexity of establishing a diagnosis along with the management option determined by the rheumatologist during the course of that visit. Because an established diagnosis—versus a new diagnosis that is not worsening—would generally require fewer tests and data to review, it would be considered less complicated. A new problem or a problem that is worsening would require more work and would be more complicated. Below are the documentation guidelines (DG) from the CMS Evaluation and Management Services Guide:
- For each encounter, an assessment, clinical impression, or diagnosis should be documented. It may be explicitly stated or implied in documented decisions regarding management plans and/or further evaluation.
- For a presenting problem with an established diagnosis, the record should reflect whether the problem is: a) improved, well controlled, resolving, or resolved; or b) inadequately controlled, worsening, or failing to change as expected.
- For a presenting problem without an established diagnosis, the assessment or clinical impression may be stated in the form of a differential diagnoses or as “possible,” “probable,” or “rule out” diagnoses.
- The initiation of, or changes in, treatment should be documented. Treatment includes a wide range of management options, including patient instructions, nursing instructions, therapies, and medications.
- If referrals are made, consultations requested, or advice sought, the record should indicate to whom or where referral or consultation is made or from whom the advice is requested.
Amount and/or Complexity of Data to be Reviewed
When guidelines talk about the amount and/or complexity of data that will be reviewed, they are referring to information gathered from sources other than the history and/or exam. This element is based on lab tests, imaging, other diagnostic tests; old records; and additional history from anyone other than the patient. Physicians receive credit or points for all data that is requested or reviewed as follows:
- Lab tests, ordered and reviewed: 1 point total for all labs
- X-rays, ordered or reviewed: 1 point total for all X-rays
- Medical tests, ordered or reviewed: 1 point total for all medical tests
- Discussing test results with performing physician: 1 point
- Obtaining old medical record/history from other sources: 1 point
- Reviewing/summarizing old medical record: 2 points
- Independent visualization: 2 points
Note that if three different lab tests are ordered, only one point is given, but if a lab test, X-ray, and old medical records are ordered, a total of three points are given, which supports a moderate level of complexity. The guidelines require that physicians record the decision to seek additional information to assist in making the best medical decision for the patient. Below are the DGs from the Evaluation and Management Services Guide:
- If a diagnostic service (test or procedure) is ordered, planned, scheduled, or performed at the time of the E/M encounter, the type of service (e.g., lab or X-ray) should be documented.
- The review of lab, radiology, and/or diagnostic tests should be documented. An entry in a progress note such as “WBC elevated” or “chest X-ray unremarkable” is acceptable. Alternatively, the review may be documented by initialing and dating the report containing the test results.
- A decision to obtain old records or additional history from the family, caretaker, or other source to supplement that obtained from the patient should be documented.
- Relevant finding from the review of old records and/or the receipt of additional history from the family, caretaker, or other source should be documented. If there is no relevant information beyond that already obtained, that fact should be documented. A notation of “old records reviewed” or “additional history obtained from family” without elaboration is insufficient.
- The results of discussion of laboratory, radiology, or other diagnostic tests with the physician who performed or interpreted the study should be documented.
- The direct visualization and independent interpretation of an image, tracing, or specimen previously or subsequently interpreted by another physician should be documented.
Risk of Significant Complications, Morbidity and/or Mortality
This element is based on the risks related to the presenting problem, diagnostic procedures, and different management options. The DGs from the Evaluation and Management Services Guide are:
- Comorbidities/underlying diseases or other factors that increase the complexity of medical decision making by increasing the risk of complications, morbidity, and/or mortality should be documented.
- If a surgical or invasive diagnostic procedure is performed at the time of the E/M encounter, the type of procedure should be documented.
- If a surgical or invasive diagnostic procedure is performed at the time of the E/M encounter, the specific procedure should be documented.
- The referral or decision to perform a surgical or invasive diagnostic procedure on an urgent basis should be documented or implied.
Many auditors believe that the MDM is what drives an E/M level. Getting to the final result of an encounter has many layers, which is why it is extremely important to document everything that is done during a visit. As a reminder: If it is not documented, it is not billed.