Conclusion
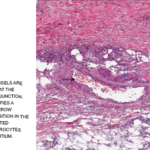
Hepatitis B-associated PAN is now rare, given the recent advances in HBV vaccination and antiviral therapies. PAN is a systemic necrotizing vasculitis that primarily affects medium-size arteries. Clinical presentation includes constitutional symptoms, neurological manifestations such as mononeuritis multiplex, and cutaneous involvement. Diagnosis encompasses checking hepatitis B serologies, inflammatory markers, angiography and biopsy of an involved site. Treatment includes a brief course of corticosteroids along with plasma exchange and antiviral therapy.
 Naveen Raj, DO, is a rheumatologist and clinical associate professor of medicine at the University of Tennessee Medical Center, Knoxville, Tenn.
Naveen Raj, DO, is a rheumatologist and clinical associate professor of medicine at the University of Tennessee Medical Center, Knoxville, Tenn.
 Lisa Duncan, MD, is an associate professor and chair of the pathology department at the University of Tennessee Medical Center, Knoxville, Tenn.
Lisa Duncan, MD, is an associate professor and chair of the pathology department at the University of Tennessee Medical Center, Knoxville, Tenn.
References
- Guillevin L, Terrier B. (2014) Oxford Textbook of Vasculitis. New York, Oxford University Press.
- Hernandez-Rodriguez J, Alba M, Prieto-Gonzalez S, et al. Diagnosis and classification of polyarteritis nodosa. J Autoimmun. 2014 Feb–Mar;48–49:84–89.
- Pagnoux C, Seror R, Henegar C, et al. Clinical features and outcomes in 348 patients with polyarteritis nodosa: A systematic retrospective study of patients diagnosed between 1963 and 2005 and entered into the French Vasculitis Study Group Database. Arthritis Rheum. 2010 Feb;62(2):616–626.
- Guillevin Loic, Mahr A, Callard P, et al. Hepatitis B virus associated polyarteritis nodosa: Clinical characteristics, outcomes, and impact of treatment in 115 patients. Medicine (Baltimore). 2005 Sep;84(5):313–322.