Figure 1B
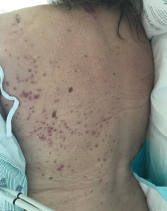
Figure 1C
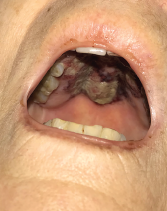
Figure 1D
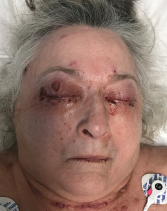
The patient presented with periorbital edema, erythematous conjunctiva, papular lesions all over her body and a mucosal ulceration on the hard palate of her oral cavity.
Mohammad A. Ursani, MD, RhMSUS, Ojas Naik, MD, Rohaan Khan & William F. Glass II, MD, PhD | Issue: February 2021 |
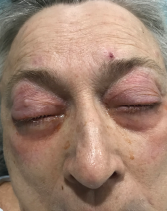
Figure 1A

Figure 1B

Figure 1C

Figure 1D
The patient presented with periorbital edema, erythematous conjunctiva, papular lesions all over her body and a mucosal ulceration on the hard palate of her oral cavity.
A biopsy of the buccal mucosa revealed stratified squamous epithelium and underlying subepithelial connective tissue with marked acute and chronic inflammation, ulceration and necrosis.
Stains for cytomegalovirus and herpes simplex virus were negative, and GMS and gram stains were negative for fungal elements and pathogenic bacteria. Mild perivascular inflammation was noted, but overt vasculitis was not seen. Features of Stevens-Johnson syndrome were also absent.
The renal biopsy revealed diffuse mesangial matrix expansion consistent with diabetic glomerulosclerosis class IIb (without nodular glomerulosclerosis) and very focal acute segmental necrotizing glomerulonephritis affecting 1 of 70 glomeruli in paraffin sections.
Immunofluorescence stains were negative for IgG, IgA, kappa light chain, lambda light chain, C3 and C1q. Weak mesangial deposition of IgM was noted. Mild tubular epithelial injury was present, and there were focal red blood cell casts. Approximately 12% of glomeruli were global sclerotic (12/99 glomeruli in the specimen), and there was 10% interstitial fibrosis with tubular atrophy.
Overall, the renal biopsy was consistent with ANCA-associated vasculitis given the presence of MPO-ANCA and the findings of pauci-immune complex deposition. However, the presence of serum anti-histone antibodies was consistent with drug-induced lupus.
The patient was treated with 1,000 mg of intravenous methylprednisolone daily for five days, then switched to 60 mg of prednisone daily and tapered thereafter. With this treatment, her hematuria and proteinuria considerably improved, and her C3 and C4 levels normalized.
Although hydralazine was discontinued, the patient’s condition remained active on a tapered dose of steroids. At that time, the patient was started on 375 mg/m2 rituximab weekly for four doses. Following this additional immunosuppression, her renal function normalized and her anemia resolved.
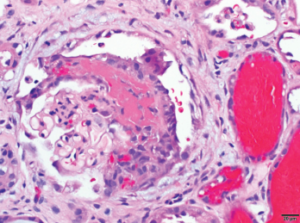
1A: Glomerulus with moderate global mesangial matrix expansion consistent with moderately advanced diabetic nephropathy (without nodular glomerulosclerosis) is noted.
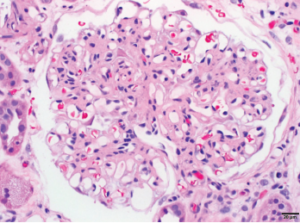
1B: Focal glomerulus with segmental fibrinoid necrosis with extracapillary proliferation and red blood cells casts consistent with necrotizing, pauci-immune, ANCA-associated glomerulonephritis are noted. Bar=20 μm.
Hydralazine is a common medication for congestive heart failure and hypertension that has been associated with systemic autoimmune conditions including drug-induced lupus, ANCA-associated vasculitis and leukocytoclastic vasculitis. It is thought that hydralazine accumulates in the intracytoplasmic neutrophilic granules, which in turn, leads to binding of myeloperoxidase and ultimately causes release of cytotoxic products and cell death. Once these neutrophils undergo cell death, antigens that are normally sequestered are exposed. This exposure leads to uptake by antigen-presenting cells, leading to production of ANCA.2,3

Hydralazine has been in use as a treatment for hypertension, most notably in heart failure patients, since 1951.1 The drug is a known cause of autoimmune disease, most specifically hydralazine-induced lupus. Hydralazine-induced lupus occurs in 7–13% of those taking the medication.2-4 It often presents with constitutional symptoms, arthritis/arthralgias, cutaneous lesions, serositis, myalgias and/or hepatomegaly. Features…
SAN DIEGO—Vasculitis expert and former editor of The Rheumatologist, Dr. Philip Seo gives us his picks for the 10 most important abstracts in ANCA-associated vasculitis to come out of ACR Convergence 2023.
The incidence of drug-induced lupus continues to rise as clinicians expand their therapeutic armamentarium. An estimated 15,000–30,000 cases of drug-induced lupus occur every year in the U.S. alone.1 It is a well-known, but rare, complication of commonly used medications, such as anti-hypertensive, anti-arrhythmic and anti-epileptic drugs, as well as biologic and immune checkpoint therapies.2,3 The…
A review of data on antinuclear antibodies and tests for rheumatoid arthritis