Following two infusions of 1,000 mg rituximab eight weeks apart, the patient’s symptoms resolved.
Supawit Srethbhakdi / shutterstock.com
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a systemic autoimmune disease that affects approximately 1% of the adult population, and involvement of extra-articular tissue occurs in approximately 40% of patients over their lifetimes.1 RA-associated pericardial disease is an uncommon complication, and surgery is the only definitive therapy—according to current literature.
In this report, we present the case of a 57-year-old man with rheumatoid factor and anti-CCP-positive RA who developed restrictive pericarditis that resolved with initiation of anti-CD20 therapy—offering a potentially novel and surgery-sparing therapy to treat a rare, highly mortal complication of RA.
The Case
A 57-year-old man presented to a general internal medicine clinic with shortness of breath and a cough that he’d had for about a month.
Four weeks prior to presentation, the patient developed worsening shortness of breath with exertion. The symptoms were stable and did not progress over the initial three weeks, but over the week prior to his presentation, he began to experience increased global fatigue with worsening dyspnea. He had an intermittent, non-productive cough. He denied a history of fever, chills, weight change, lightheadedness, exertional chest discomfort, palpitations, orthopnea, paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea, lower extremity edema, cough, wheeze, focal weakness or myalgia.
Medical history: The patient’s medical history was significant for RA—he was diagnosed at age 53—complicated by interstitial lung disease (ILD), for which he was taking 20 mg of methotrexate weekly and 50 mg of etanercept weekly. He also has Graves’ disease, complicated by ophthalmopathy, for which he was taking 10 mg of methimazole daily. He suffers from depression and anxiety, for which he was taking 40 mg of citalopram daily, 150 mg of buproprion twice daily and 0.5 mg of lorazepam as needed.
Physical examination: The patient’s physical examination was notable for inspiratory crackles at the left base posteriorly with an elevated jugular venous pressure but no evidence of pulsus paradoxus.
Laboratory tests & imaging: Results of his laboratory evaluation were notable for interval elevation of his previously normal C-reactive protein and sedimentation rate, as well as his pro-brain natriuretic peptide level (see Table 1).
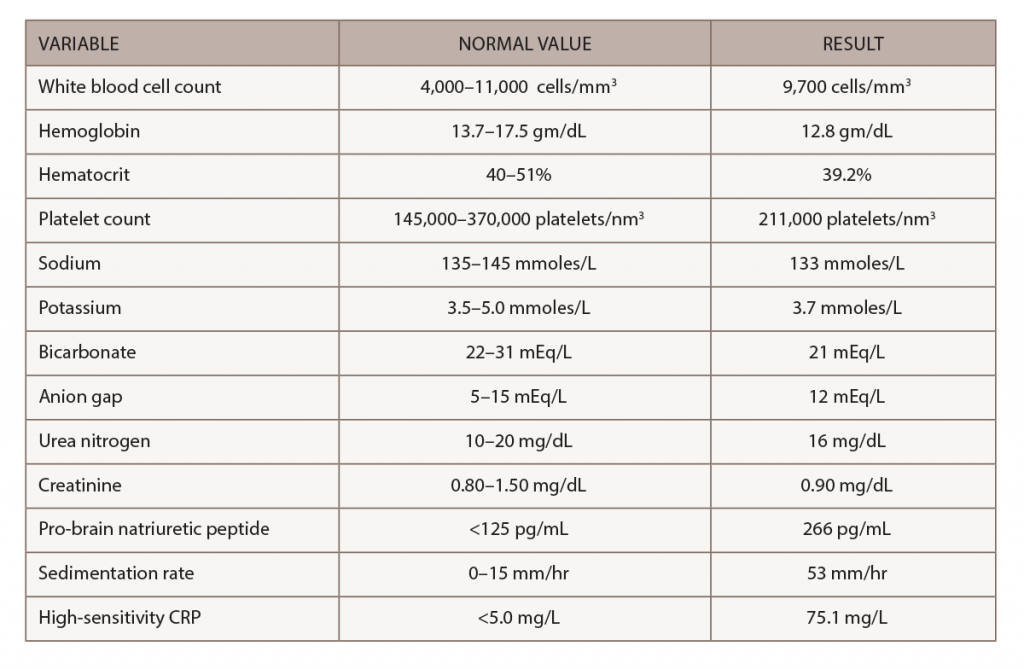
A chest X-ray demonstrated interval enlargement of the cardiomediastinal silhouette, with increased bilateral hilar, and vascular markings concerning for pulmonary edema with small bilateral pleural effusions.
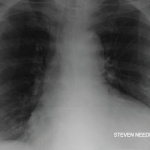
An electrocardiogram showed a normal sinus rhythm at a rate of 80 beats per minute with normal intervals and diffuse low voltage. An echocardiogram revealed a moderate, circumferential pericardial effusion with subtle right ventricular diastolic collapse and less than 50% respiratory change in the inferior vena cava, consistent with elevated right atrial pressures.
Clinical Course
The patient was referred to a cardiologist after his initial presentation, and ultimately the patient deferred admission for pericardiocentesis, preferring outpatient therapy with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and colchicine for presumed restrictive pericarditis.
At his one-month follow-up appointment, the patient reported the intervals between bouts of shortness of breath, associated with new-onset hypoxemia, were shorter. Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) was obtained on an emergent basis. It demonstrated thickening of the visceral and parietal pericardium with a moderate effusion, concerning for worsening of his previously demonstrated restrictive pericarditis. The MRI was also notable for mild left ventricular hypokinesis. Consequently, the patient was admitted to the cardiology unit for a right and left heart catheterization. Intrathoracic intraventricular dissociation and a positive Kussmaul sign consistent with restrictive physiology were noted.
A surgeon was consulted to discuss a potential pericardiectomy, but the procedure was considered to be high risk for the patient given concurrent active inflammatory disease and his known history of interstitial lung disease with a new left-sided effusion of unclear etiology.
The patient subsequently had a thoracentesis performed. The fluid studies showed a lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) level of 1,886 IU/L, protein of 4.6 g/dL and glucose <2 mg/dL. The infectious workup was negative. The results were consistent overall with an inflammatory effusion likely secondary to his poorly controlled RA.
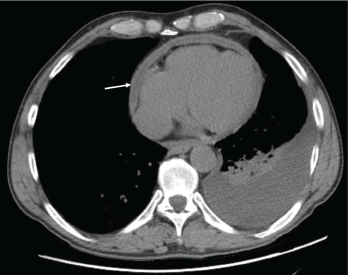
Figure 1: Pericardial effusion demonstrated on a CT of the chest. The arrow indicates the effusion.
With the input of the rheumatologist, the patient was started on rituximab infusions, and after two infusions of 1,000 mg eight weeks apart, the patient’s symptoms had resolved, his echocardiogram and inflammatory markers had normalized, and a repeat computed tomography (CT) of his chest (see Figures 1 and 2) demonstrated near-total resolution of his pericardial thickening.
The patient is currently asymptomatic and continues to receive rituximab infusions as needed (every six or 12 months) while on long-term, low-dose prednisone.
Discussion
Left untreated, RA is progressive and can lead to deterioration of cartilage and bone in the affected joints, ultimately leading to permanent disability. Involvement of extra-articular tissue occurs in approximately 40% of patients with RA and is associated with a higher mortality.1
Symptomatic pericarditis secondary to RA is uncommon, occurring in less than 10% of RA patients, but approximately 30–50% of patients have evidence of pericardial involvement on autopsy.
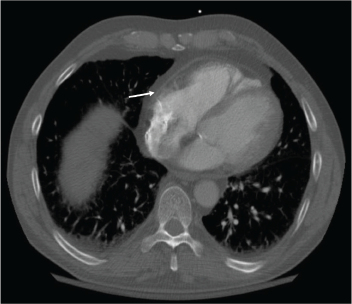
Figure 2: Resolution of the pericardial effusion was indicated on the chest CT obtained two months after initiation of rituximab infusions.
Symptomatic pericarditis secondary to RA is uncommon, occurring in less than 10% of RA patients, but approximately 30–50% of patients have evidence of pericardial involvement on autopsy.2 Episodes of tamponade and restrictive pericarditis in RA occur infrequently, and the current literature is limited to case reports.3,4 Based on current reports, surgery is the only definitive therapy known to reverse the pericardial remodeling and tamponade physiology in this patient population, and medical therapy is thought to be largely ineffective. Thus, our case presents a potentially new therapy to address a rare, but highly morbid condition.
Recent studies support a potentially effective role for rituximab in patients with active disease while on methotrexate or anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy, demonstrating that a single course of rituximab can result in clinically significant improvements in quality of life and radiographically identified disease progression within as little as 24 weeks.5 These studies were limited to patients with active articular disease, but based on our patient and his rapid recovery after initiating rituximab infusions, it is possible that anti-CD20 therapy could be a potential surgery-sparing alternative for patients with life-threatening pericardial disease.
 Scott Rodriguez, MD, is an internal medicine resident at Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center, N.H.
Scott Rodriguez, MD, is an internal medicine resident at Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center, N.H.
 Daniel Albert, MD, is a professor of medicine and pediatrics in the Section of Rheumatology at Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center and the Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth. He is also a professor in the Dartmouth Institute of Health Policy and Clinical Practice. He specializes in rheumatic disease of adults and children.
Daniel Albert, MD, is a professor of medicine and pediatrics in the Section of Rheumatology at Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center and the Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth. He is also a professor in the Dartmouth Institute of Health Policy and Clinical Practice. He specializes in rheumatic disease of adults and children.
 Kenton Powell, MD, is an internal medicine physician at Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center, an assistant professor of medicine at Geisel Medical School at Dartmouth, program director of the Primary Care Track Internal Medicine Residency Program and associate program director of Categorical Track Internal Medicine Residency Program.
Kenton Powell, MD, is an internal medicine physician at Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center, an assistant professor of medicine at Geisel Medical School at Dartmouth, program director of the Primary Care Track Internal Medicine Residency Program and associate program director of Categorical Track Internal Medicine Residency Program.
References
- Turesson C, O’Fallon WM, Crowson CS, et al. Occurrence of extraarticular disease manifestations is associated with excess mortality in a community based cohort of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2002 Jan;29(1):62–67.
- Guedes C, Bianchi-Fior P, Cormier B, et al. Cardiac manifestations of rheumatoid arthritis: A case-control transesophageal echocardiography study in 30 patients. Arthritis Rheum. 2001 Apr;45(2):129–135.
- Romanoff H, Rozin R, Zlotnick A. Cardiac tamponade in rheumatoid arthritis. A case report and review of the literature. Arthritis Rheum. 1970 Jul–Aug;13(4):426–435.
- Thould AK. Constrictive pericarditis in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1986 Feb;45(2):89–94.
- Cohen SB, Emery P, Greenwald MW, et al. Rituximab for rheumatoid arthritis refractory to anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy: Results of a multicenter, randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, phase III trial evaluating primary efficacy and safety at twenty‐four weeks. Arthritis Rheum. 2006 Sep;54(9):2793–2806.