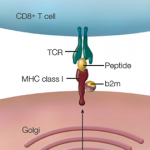
 Axial spondyloarthritis (SpA), an inflammatory disease of the spine and sacroiliac joints, causes new bone formation that may lead to total ankylosis of the spine. Laura C. Coates, MBChB, PhD, associate professor of rheumatology at the University of Oxford, U.K., and colleagues sought to describe the relationship between the presence of HLA-B27 and the radiographic phenotype of axial SpA. They found patients with axial SpA who were positive for HLA-B27 had more severe radiographic damage than patients who were negative for HLA-B27. These HLA-B27-positive individuals also had more marginal syndesmophytes and more frequent syndesmophyte symmetry than those who were negative for HLA-B27. The investigators published their findings in the June 2021 issue of Arthritis Care & Research.1
Axial spondyloarthritis (SpA), an inflammatory disease of the spine and sacroiliac joints, causes new bone formation that may lead to total ankylosis of the spine. Laura C. Coates, MBChB, PhD, associate professor of rheumatology at the University of Oxford, U.K., and colleagues sought to describe the relationship between the presence of HLA-B27 and the radiographic phenotype of axial SpA. They found patients with axial SpA who were positive for HLA-B27 had more severe radiographic damage than patients who were negative for HLA-B27. These HLA-B27-positive individuals also had more marginal syndesmophytes and more frequent syndesmophyte symmetry than those who were negative for HLA-B27. The investigators published their findings in the June 2021 issue of Arthritis Care & Research.1
Study Design
The large international, observational, cross-sectional study included a mixed population of individuals with axial psoriatic arthritis (PsA; n=244) and ankylosing spondylitis (AS; n=198) from eight sites in Europe and North America. The investigators gathered basic demographic data, a recent patient-completed disease activity measure (the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index [BASDAI]) and a recent measure of C-reactive protein (CRP).
One-quarter of the patients with PsA tested positive for HLA-B27, and three-quarters of the patients with AS were positive for HLA-B27. Patients who were HLA-B27 positive had a mean age of 49.1 ± 14.2 years, whereas patients who were HLA-B27 negative had a mean age of 53.8 ± 13.8 years. HLA-B27 positive patients were also more likely to be male (73%) than HLA-B27 negative patients (59%). HLA-B27 positive patients had disease duration of 13.6 ± 11.9 years, whereas HLA-B27 negative patients had a disease duration of 11.0 ± 10.2 years. Lastly, patients who were HLA-B27 positive had a mean BASDAI score of 4.1 ± 2.0 compared with a mean BASDAI score of 3.5 ± 2.4 for HLA-B27 negative patients. All of these differences were statistically significant.
Study Results
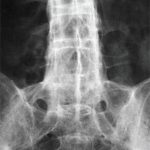
Blinded to the clinical details, the investigators read the radiographs by consensus in a single, central location. They recorded the symmetry of the sacroiliac joints and lumbar syndesmophytes and the morphology of the syndesmophytes, together with the modified Stoke Ankylosing Spondylitis Spine Score (mSASSS) and the Psoriatic Arthritis Spondylitis Radiographic Index (PASRI). The mSASSS evaluates the corners of the vertebral bodies from the lower border of C2 to the upper border of T1 and from the lower border of T12 to the upper border of S1. The PASRI evaluates the vertebral bodies and the zygo-apophyseal joints at C2/C3, C3/C4 and C4/C5 for fusion. The PASRI also scores the sacroiliac joints.