a. Yes, with a prevalence greater than that of the general population
b. No, with a prevalence less than that of the general population
c. No, with a prevalence equal to that of the general population
Gout can occur in patients with RA, but at a lower prevalence than that of the general population (2.4% vs. 5.2% over 25 years).4 Given the increased risk of joint destruction and clinical overlap, it is important to confirm the diagnosis of gout. Uncontrolled obesity, alcohol use and kidney disease increase the risk of developing gout.
This patient was diagnosed with RA five years prior to admission on the basis of scleritis in the setting of a positive rheumatoid factor and cyclic citrullinated peptide. Because the patient was transitioning care, many past diagnoses remained fixed in his medical history. The patient had been diagnosed with gout many years earlier; however, he was never placed on a consistent uricosuric regimen and was actively treated only for RA.
After failing therapy with methotrexate, hydroxychloroquine, infliximab and tocilizumab, based on persistent symptoms and side effects, the patient was placed on abatacept as a long-term treatment regimen. His primary presentation on admission heightened concern for infection in the setting of active immune suppression.
Despite adjusting medications, in a five-year span, the patient had 15 clinical visits in which he described either mono- or polyarthritis. His persistent joint stiffness and limited range of motion in some joints despite treatment with abatacept led his clinicians to consider gout.
There are several documented instances in which this patient continued to demonstrate worsening arthralgia, despite medical therapy for RA. For example, he presented with synovitis of his right proximal interphalangeal joint and an elbow bursitis (CDAI score of 33). He was treated with prednisone for a presumed RA flare despite continued therapy on abatacept. Over the course of several months, his ongoing joint pain, which was refractory to abatacept and steroids, was considered to be due to his RA. A more diligent review of his persistent joint pain led to the diagnosis of gout.
In October 2015, the patient was to have left ankle surgery for erosive RA. In that time, the patient continued to complain of swelling in fingers and left wrist without significant improvement on his medications. Shortly after, the patient was admitted to the hospital as mentioned above.
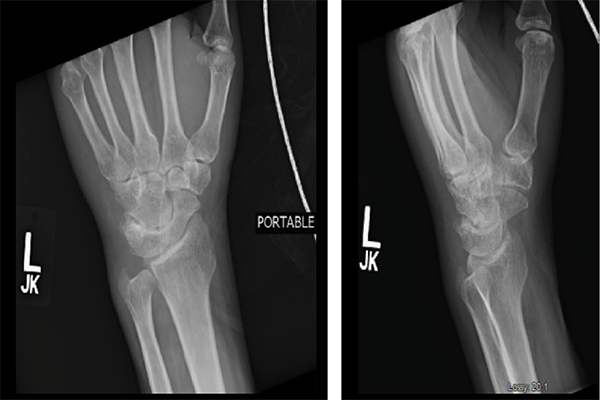
Figures 3 & 4: X-rays of the Left Wrist
Question 6
Is anchoring bias more prevalent in patients with many co-morbidities?


