Table 2: Abnormal Laboratory Findings of IgG4-RKD
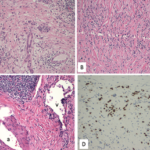
IgG4-related TIN (IgG4-RTIN) can be diagnosed using the organ-specific diagnostic criteria for IgG4-RKD. Characteristic histopathological findings of IgG4-RD include dense lymphoplasmacytic infiltration, which must be accompanied by >10 IgG4+ plasma cells/high power field (HPF) and/or IgG4+/IgG+ plasma cells >40%, and characteristic storiform fibrosis surrounding nests of lymphocytes and/or plasma cells (see Table 3). Therefore, lymphoplasmacytic TIN with sclerofibrosis and prominent IgG4-positive plasma cells appears to be a representative histological finding of IgG4-RKD.7,8 Other features useful for establishing a diagnosis include obliterative phlebitis, lesions extending into the renal capsule, eosinophil infiltration, well-defined regional lesion distribution and marked fibrosis (see Table 3). The histological findings in extra-renal organs include dense lymphoplasmacytic infiltration by >10 IgG4+ plasma cells/HPF, and/or IgG4+/IgG+ plasma cells >40%.8
Kawano et al. proposed diagnostic criteria for IgG4-RKD based on previously established diagnostic criteria for autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP).9 A diagnosis of IgG4-RKD is definitive in patients with organ enlargement, mass or nodular lesions, and/or organ dysfunction, serum IgG4 concentration >135 mg/dL and histopathological findings of >10 IgG4 cells/HPF and/or an IgG4+/IgG+ cell ratio >40% or characteristic fibrosis (see Table 4A). The diagnosis is probable in the presence of abnormal urinalysis or decreased kidney function with either elevated serum IgG4 levels, low complements or elevated serum IgE levels, and histological findings of >10 IgG4 cells/HPF and/or IgG4+/IgG+ cell ratio >40% or characteristic fibrosis. IgG4-RKD is also likely when abnormal renal radiologic findings are present, along with characteristic histologic findings in the kidney or extra-renal organs.
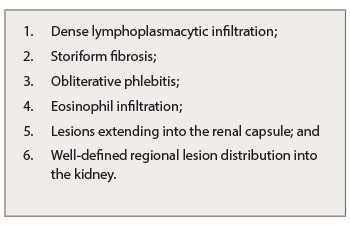
Table 3: Characteristic Histopathological Findings of IgG4-RKD
Finally, the diagnosis is probable when elevated serum IgG4 levels and histologic findings in the kidney are present (see Table 4B, p. 18). The diagnosis is possible when the presence of some kidney damage or abnormal renal radiologic findings are combined with either elevated serum IgG4 level or histological findings of >10 IgG4 cells/HPF and/or IgG4+/IgG+ cell ratio >40% (see Table 4C).10,11
Kidney Manifestations of IgG-RKD
Isolated kidney IgG4 disease has been reported and presents as multiple low-attenuation cortical nodules, wedge-shape lesions or diffuse patchy areas that may be associated with impaired renal function.10 The renal manifestation of IgG4-RD is, in most cases, tubulointerstitial, but sometimes may associate glomerular involvement, especially membranous nephropathy (MN), which could be also found as an isolated lesion (see Table 5).11
IgG4-RTIN can be focal or diffuse, and sometimes presents with tumor-like masses.12 Cystic dilatation of ducts can occur secondary to obstruction or stenosis of collecting ducts due to storiform or bird’s eye fibrosis.13 Obliterative phlebitis is an uncommon finding in kidney biopsy specimens because medium-size veins are rarely sampled.14 Only one case of IgG4-related renal arteritis has been described (see Table 5).15 Electron-dense deposits can be seen involving the tubular basement membrane.16 Immune complex deposits consist predominantly of IgG, C3, kappa and lambda light chains on immunofluorescence.17 In most cases, focal mild mononuclear cell tubilitis occurs, but eosinophilic or plasma cell tubulitis may also be seen.