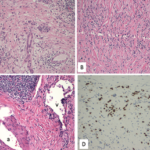
In RF, the fibrotic lesion is macroscopically a firm white plaque around the abdominal aorta, illiacal vessels and ureters, whereas at the microscopic level, proliferation of fibroblasts and deposition of extracellular matrix may be noted. This fibro-inflammatory process results to hyalinization of the collagen.29
Other Organ Manifestations
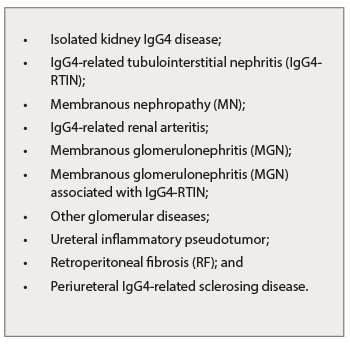
Table 5: Kidney Manifestations
of IgG4-RKD
Isolated IgG4-RKD remains uncommon.45 Most patients suffer multiorgan involvement. The most common extra-renal lesions include AIP, sialadenitis and dacryoadenitis (see Table 6).30
Sarles et al. first described AIP as a “chronic inflammatory sclerosis of the pancreas” in 1961.31 The different diagnostic criteria for AIP include imaging, laboratory, histopathology findings and response to steroid therapy. The Japan Pancreas Society (JPS) criteria, the Kim criteria, the HISORt criteria and the Italian criteria are used worldwide.32,33 The JPS, Kim and HISORt criteria are image based and include diffuse narrowing of the main pancreatic duct and diffuse enlargement of the pancreas with delayed (rim) enhancement. The laboratory criteria include elevated levels of serum gammaglobulins, elevated serum IgG4 and the presence of autoantibodies.34 All worldwide criteria employ the histopathology criteria, the response to steroid therapy and the association with either other organ involvement (biliary strictures, parotid/lacrimal gland involvement, mediastinal lymphadenopathy and RF) or other autoimmune diseases (such as ulcerative colitis, Crohn’s disease, sclerosing cholangitis, primary biliary cirrhosis and Sjӧgren’s syndrome [SS]). The histopathology criteria demonstrate marked lymphoplasmocytic sclerosing pancreatitis or lymphoplasmocytic infiltrate with dense fibrosis in the pancreas, or dense lymphocytic infiltration and destruction of the exocrine glands on histology.32,33,34
Hamano et al. reported that a level of IgG4 of 135 mg/dL and higher could differentiate AIP from pancreatic cancer, with a sensitivity of 95% and a specificity of 97%.28 The clinical manifestations can vary from a mild, acute recurrent pancreatitis, abdominal pain, anorexia and weight loss, to painless obstructive jaundice due to biliary stricture or a pancreatic mass.35
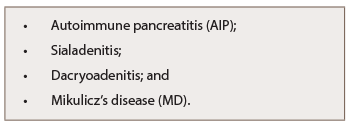
Table 6: Other Organ Manifestations of IgG-RKD
Mikulicz’s disease (MD), originally reported by Johann von Mikulicz-Radecki in 1892, is characterized by symmetric and persistent swelling of the lacrimal and salivary glands (see Table 6). MD has been recognized as a subtype of SS, which is a chronic form of dacryoadenitis and sialoadenitis. Mikulicz’s-type dacryoadenitis and sialoadenitis is associated with an elevated serum IgG4 level and fibrosis with significant infiltration of IgG4-positive plasma cells.36 Mavragani et al. found raised IgG4 serum levels in 7.5% of primary SS patients in association with IgG4-RD clinical, serologic and histopathologic features.37