For this study (currently open for enrollment and listed under identifier NCT03221257), patients with SSc-ILD are randomized to either treatment with mycophenolate alone or treatment with mycophenolate plus pirfenidone for 18 months. A prior open-label study demonstrated that pirfenidone is safe in patients with SSc-ILD. In that four-month study, patients were randomized in a 1:1 ratio to receive pirfenidone titrated over two or four weeks from a starting dose of 801 mg/day up to a maintenance dose of 2,403 mg/day. Mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) was combined with pirfenidone in 63.5% of patients with good tolerability, and the four-week dosage titration for pirfenidone was better tolerated than a two-week titration.9
SLS III is targeting SSc-ILD patients who live in North America and are treatment naive or early in their treatment course with MMF (i.e., treatment with MMF for 24 or fewer weeks prior to enrollment). This approach, combining both drugs up front, is designed to take advantage of the rapid onset of a treatment effect that has been observed when pirfenidone is used to treat idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (not related to scleroderma). In contrast, we know from SLS II that the improvements in pulmonary function occur in a delayed manner when using MMF alone.
The hope: This early combination therapy will provide both a faster and synergistic effect of treatment on the course of FVC percent-predicted.
To date, no clinical trials in SSc-ILD patients have assessed the safety and efficacy of randomized treatment with an anti-fibrotic agent and an immunosuppressant agent. Although the SENSCIS trial (which compared nintedanib with placebo for SSc-ILD) allowed patients to be on background mycophenolate before and during the trial (or not), patients were not specifically randomized to combination, nor was the dosing of the mycophenolate standardized; the study showed statistically significant, but modest, change favoring nintedanib
Nintedanib in the annual rate of decline in FVC, with no improvement in skin score and patient-reported outcomes.10
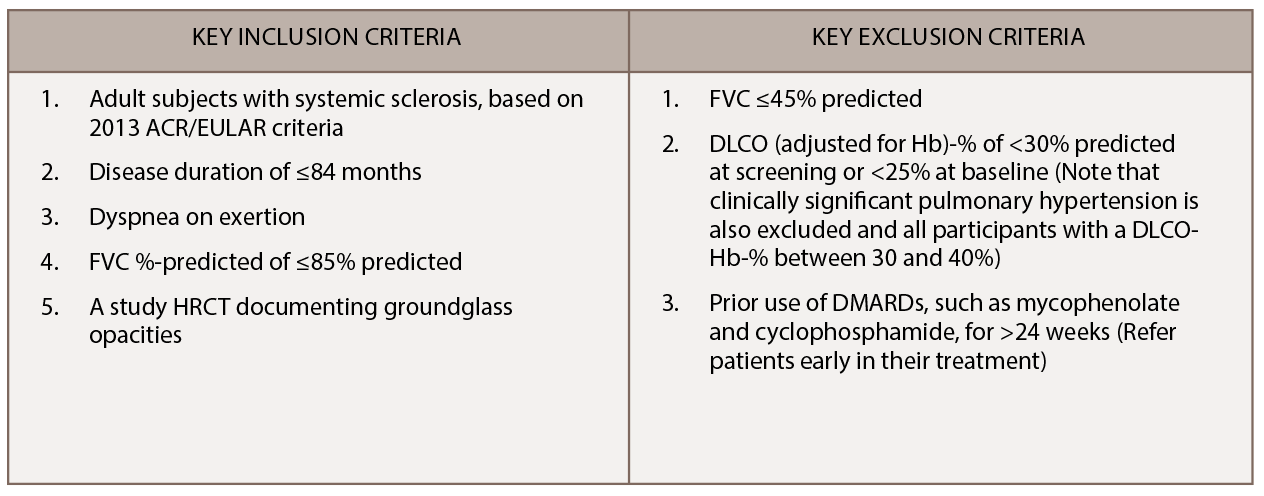
We are recruiting additional sites in the U.S. and Canada for SLS III, with 16 active scleroderma centers currently participating in this trial. Learn more. SLS III is an investigator initiated trial funded by Genentech. The key entry criteria for SLS III appear in Table 1.
 Elizabeth R. Volkmann, MD, MS, is an assistant professor of medicine in the Division of Rheumatology at the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA). She is the founder and co-director of the UCLA Connective Tissue Disease-Interstitial Lung Disease Program. She cares and advocates for patients with systemic sclerosis and autoimmune lung disease and is an active clinical and translational researcher in these areas.
Elizabeth R. Volkmann, MD, MS, is an assistant professor of medicine in the Division of Rheumatology at the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA). She is the founder and co-director of the UCLA Connective Tissue Disease-Interstitial Lung Disease Program. She cares and advocates for patients with systemic sclerosis and autoimmune lung disease and is an active clinical and translational researcher in these areas.