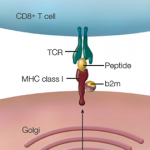
In the 1970s, Japanese researchers reported that Takayasu arteritis is associated with the human leukocyte antigen (HLA) region of chromosome 6, which encodes a variety of cell-surface proteins that help regulate the immune system.2 Subsequently, researchers linked the disease to a specific variant of the HLA class B gene, known as the HLA-B*52 allele, which encodes one of these immune system-regulating cell-surface proteins.
“There was always a question whether or not other genes outside the HLA region might be contributing,” Dr. Sawalha says. Then in 2013, he and colleagues conducted a genome-wide association study that used an unbiased approach to scan the genomes of more than 450 patients and look for differences compared with healthy controls.3 The study searched for genetic variants, mainly in the form of single-letter changes in the DNA known as single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), which occur with a significantly higher frequency in people with Takayasu arteritis than in healthy counterparts.
The study not only confirmed the Takayasu arteritis association with HLA-B*52 but also identified several new associations with small parts of the human genome beyond that HLA region. Akin to neighborhoods, these genetic susceptibility loci are stretches of DNA that may include multiple genes. From that initial effort and another four large-scale genetic studies, researchers have found Takayasu arteritis associations with 18 genetic susceptibility loci so far.
“So we’ve gone a long way from only having the HLA-B*52 connection to now having a number of genetic susceptibility loci within the HLA and also outside of the HLA,” Dr. Sawalha says. “That helps us understand the disease better, especially from the immunologic standpoint, but we are still not there yet. We still have much more work to do.”
Closer Genetic Associations
One pressing task has been figuring out which genes within each genetic susceptibility loci are truly associated with Takayasu arteritis. “We take these regions and try to identify, as much as we can, what might be the causal variant—the causal gene—and how it might affect the cause of the disease,” Dr. Sawalha says. In the review paper, he and Dr. Casares-Marfil used several methods to help determine these causal relationships with more precision. Within each genetic neighborhood, or locus, the researchers tried to determine which genetic variants were consistently associated with Takayasu arteritis. From those candidates, they asked which were associated with unusually higher or lower gene activity in disease-relevant cells and tissues, like in immune cells and tissue from the aorta.