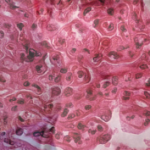
Although the advent of the MMF era has brought forth important gains for black patients in particular, many questions remain unanswered. Will advances in our understanding of genetics lead to the identification of new genetic contributors to severe lupus? Recent studies suggest that alleles of APOL1 that are commonly found in individuals of African heritage may be strong predictors of ESRD from lupus nephritis.12 Similarly, early evidence suggests that there may be a genetic contribution to the rates of MMF metabolism that may predispose black patients to a lack of response to MMF therapy. Can we glean new knowledge about the role of socioeconomic and environmental factors that contribute to worsening lupus?
These differences may now be more apparent, given our greater understanding of the racial differences in response to therapy. The issues of access and adherence to therapy strategies remain poorly addressed topics. Can we improve access to, and delivery of, care by adapting strategies developed in the fight against HIV for lupus patients?
As we enter the era of personalized medicine, we will ultimately have to develop approaches that account for the various genetic, social and environmental factors and are tailored to the needs of the individual patient.
Eric L. Wise, MD, is a rheumatologist in Ann Arbor, Mich.
W. Joseph McCune, MD, is a rheumatologist at the University of Michigan, in Ann Arbor, Mich., and was recognized as a Master by the ACR in 2014.
References
- Chakravarty EF, Bush TM, Manzi S, et al. Prevalence of adult systemic lupus erythematosus in California and Pennsylvania in 2000: Estimates obtained using hospitalization data. Arthritis Rheum. 2007 Jun;56(6):2092–2094.
- Fessel WJ. Systemic lupus erythematosus in the community. Incidence, prevalence, outcome, and first symptoms; the high prevalence in black women. Arch Intern Med. 1974 Dec;134(6):1027–1035.
- Kaslow RA, Masi AT. Age, sex, and race effects on mortality from systemic lupus erythematosus in the United States. Arthritis Rheum. 1978 May;21(4):473–479.
- Ward MM. Changes in the incidence of endstage renal disease due to lupus nephritis in the United States, 1996–2004. J Rheumatol. 2009 Jan;36(1):63–67.
- Austin HA 3rd, Boumpas DT, Vaughan EM, et al. High-risk features of lupus nephritis: Importance of race and clinical and histological factors in 166 patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1995;10(9):1620–1628.
- Cooper GS, Parks CG, Treadwell EL, et al. Differences by race, sex and age in the clinical and immunologic features of recently diagnosed systemic lupus erythematosus patients in the Southeastern United States. Lupus. 2002;11(3):161–167.
- Alarcon GS, Calvo-Alén J, McGwin G Jr., et al. Systemic lupus erythematosus in a multiethnic cohort: LUMINA XXXV. Predictive factors of high disease activity over time. Ann Rheum Dis. 2006 Sep;65(9):1168–1174.
- Reveille JD, Moulds JM, Ahn C, et al. Systemic lupus erythematosus in three ethnic groups: I. The effects of HLA class II, C4, and CR1 alleles, socioeconomic factors, and ethnicity at disease onset. LUMINA Study Group. Lupus in minority populations, nature versus nurture. Arthritis Rheum. 1998 Jul;41(7):1161–1172.
- Barr RG, Seliger S, Appel GB, et al. Prognosis in proliferative lupus nephritis: The role of socio-economic status and race/ethnicity. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2003 Oct;18(10):2039–2046.
- Richman IB, Taylor KE, Chung SA, et al. European genetic ancestry is associated with a decreased risk of lupus nephritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2012 Oct;64(10):3374–3382.
- Isenberg D, Appel GB, Contreras G, et al. Influence of race/ethnicity on response to lupus nephritis treatment: The ALMS study. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2010 Jan;49(1):128–140.
- Freedman BI, Langefeld CD, Andringa KK, et al. End-stage renal disease in African Americans with lupus nephritis is associated with APOL1. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014 Feb;66(2):390–396.