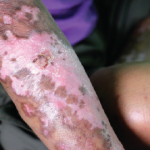
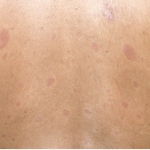
Further Investigations of DPP4 Inhibitors
Dr. Soare notes that the potent antifibrotic effects of DPP4 inhibitors may have direct translational implications. DPP4 inhibitors have already been shown to have a good tolerability and safety profile, making them an attractive target for clinical investigation. In 2006, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved the use of oral DPP4 inhibitors to treat type 2 diabetes. DPP4 inhibitors increase the levels of active insulinotropic polypeptide and glucagon-like peptide-1, resulting in stimulation of insulin and inhibition of glucagon.6 Data from other clinical studies has shown promising results for DPP4 inhibitors in other disease states, such as renal disease.7
“To prove the effect in patients with systemic sclerosis, it would definitely be interesting to test DPP4 inhibitors in a clinical trial,” says Dr. Soare. “Using the data from the post-marketing studies available in patients with type 2 diabetes treated with DPP4 inhibitors would speed up the process of approval of these agents for another indication.”
DPP4 inhibitors are not the only components of the TGF-β pathway that researchers have pursued. In 2015, researchers reported promising results of a phase 2 trial of systemic sclerosis patients with fresolimumab, an inhibitor of all three isoforms of TGF-β.8 Dr. Soare points out that in contrast to fresolimumab, inhibiting DPP4 expression would not affect all downstream signaling pathways of TGF-β. This might make it more suitable for use in light of its side effect profile.
Clinical trials are needed before any strong conclusions can be drawn. However, DPP4 inhibitors may represent a new avenue of hope for this devastating disease.
Ruth Jessen Hickman, MD, is a graduate of the Indiana University School of Medicine. She is a freelance medical and science writer living in Bloomington, Ind.
References
- Soare A, Györfi HA, Matei AE, et al. Dipeptidylpeptidase 4 as a marker of activated fibroblasts and a potential target for the treatment of fibrosis in systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020 Jan;72(1):137–149.
- Zent J, Guo LW. Signaling mechanisms of myofibroblastic activation: Outside-in and inside-out. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;49(3):848–868.
- Ayers NB, Sun CM, Chen SY. Transforming growth factor-β signaling in systemic sclerosis. J Biomed Res. 2018 Jan 26;32(1):3–12.
- Rinkevich Y, Walmsley GG, Hu MS, et al. Skin fibrosis. Identification and isolation of a dermal lineage with intrinsic fibrogenic potential. Science. 2015 Apr 17;348(6232):aaa2151.
- Beyer C, Distler JH. Tyrosine kinase signaling in fibrotic disorders: Translation of basic research to human disease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Jul;1832(7):897–904.
- Drucker DJ. Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibition and the treatment of type 2 diabetes: Preclinical biology and mechanisms of action. Diabetes Care. 2007 Jun;30(6):1335–43.
- Kanasaki K. The role of renal dipeptidyl peptidase-4 in kidney disease: Renal effects of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors with a focus on linagliptin. Clin Sci (Lond). 2018 Feb 28;132(4):489–507.
- Rice LM, Padilla CM, McLaughlin SR, et al. Fresolimumab treatment decreases biomarkers and improves clinical symptoms in systemic sclerosis patients. J Clin Invest. 2015 Jul 1;125(7):2795–2807.