Universal Reporting

Dr. Singh
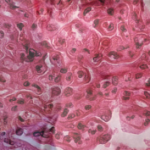
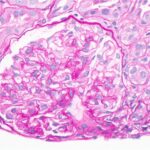
The study also examined whether the burden of renal arteriosclerosis is under-reported in LN biopsies by over-reading renal biopsies in a subset of 42 patients using the Banff criteria for grading. The Banff grading system categorizes renal arteriosclerosis as none, mild (<25%), moderate (26–50%), and severe (>50%) luminal narrowing. Patients included in this analysis had a mean age of 31 years at the time of their LN diagnosis, most were women (75%), a minority were Black (25%), and nearly half (49%) had chronic LN.
When comparing these readings to the original pathology reports, the investigators found that >50% of the original reports missed renal arteriosclerosis and nearly 40% lacked details on arteriosclerosis or arterial changes.
Although the positive predictive value of the routine pathology reporting was 80% in the study, the over-read analysis using the Banff criteria showed that the assessment of arteriosclerosis in LN biopsies is under-reported.
“Our study underscores a need for universal use of systemic Banff renal arteriosclerosis grading criteria in all LN biopsies, similar to transplant pathology reporting standards,” says Dr. Garg.
Dr. Singh believes more emphasis will now be placed on looking for renal arteriosclerosis in LN patients, given the findings of the study. He urges clinicians to ask pathologists to comment on the presence or absence of renal arteriosclerosis when examining kidney biopsies from LN patients.
“The increased awareness that the presence of arteriosclerosis in kidney biopsies from patients with lupus nephritis predicts future development of cardiovascular disease will lead to increased reporting of arteriosclerosis on kidney biopsies,” Dr. Singh predicts.
Mary Beth Nierengarten is a freelance medical journalist based in Minneapolis.
References
- Garg S, Bartels CM, Hansen KE, et al. High burden of premature arteriosclerosis on renal biopsies in incidence lupus nephritis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken).
2020 Jan 7. doi: 10.1002/acr.24138. [Epub ahead of print] - Garg S, Panzer S, Hansen K, et al. Renal arteriosclerosis predicts cardiovascular disease in lupus nephritis [abstract 1564]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019;71(suppl 10).
- Myllymäki J, Syrjänen J, Helin H, et al. Vascular diseases and their risk factors in IgA nephropathy. Nephrol Dial Transplant.
2006;21(7):1876–82. - Myllymäki J, Honkanen T, Syrjänen J, et al. Uric acid correlates with the severity of histopathological parameters in IgA nephropathy. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2005;20(1):89–95.
- Loupy A, Vernerey D, Viglietti D, et al. Determinants and Outcomes of accelerated arteriosclerosis: Major impact of circulating antibodies. Circ Res. 2015;117(5):470–482.