The two internal organs that have the greatest influence on the survival of patients with pSS are the lungs and the kidneys. SS-related pulmonary disease is clearly associated with worsened quality of life and poorer survival, with a two- to four-fold increase in the risk of death compared with patients without pulmonary disease.3 With respect to renal involvement, a recent study, including 35 patients with biopsy-proven renal involvement, found high rates of adverse outcomes, including chronic renal failure (31%), lymphoma (26%) and death (26%), especially in patients with cryoglobulinemic glomerulonephitis.3,10
IgG4-Related Disease, the Great Mimicker
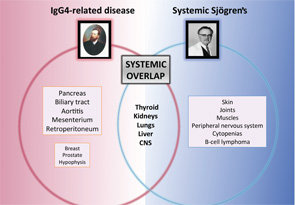
Some systemic diseases may mimic the clinical picture of systemic Sjögren’s through tissue infiltration by granulomas (i.e., sarcoidosis), amyloid proteins (i.e., amyloidosis) or malignant cells (i.e., hematologic neoplasia). However, a new disease was recently added to infiltrative diseases that may mimic systemic Sjögren’s. IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is a systemic immune-mediated disease that has been previously described in Japan and is characterized by tissue infiltration of IgG4-bearing plasma cells.11 It is not a new disease, because many previously recognized conditions of unknown etiology and pathogenesis formerly regarded as entirely disparate disorders are now considered to comprise parts of the IgG4-RD spectrum, including Mikulicz disease, Küttner’s tumor and Riedel thyroiditis, among others.
Major salivary glands are among the organs more frequently involved in the IgG4-related disease, reported in 40% of cases.12 Involvement of internal organs is common and may lead to organ failure or severe systemic impairment, particularly in the pancreas, liver and biliary tree, kidneys, thyroid gland, lungs and aorta. A significant number of these organ-specific involvements are common with pSS, including renal, pulmonary, hepatic, thyroid and central nervous system disease (see Figure 2). A specific evaluation for IgG4 disease should be considered for patients with pSS who present with pancreatic signs, renal disease or interstitial pulmonary involvement.
Systemic Therapies: Targeting B Cells
Systemic therapy should be tailored to the organ involved and the severity of the condition, although no controlled trials in pSS guide their use.13 For patients with moderate systemic involvement, including arthritis, non-complicated cutaneous purpura or non-severe peripheral neuropathy, prednisone (<0.5 mg/kg/d) may suffice. For patients with internal organ involvement (e.g., pulmonary alveolitis, glomerulonephritis or severe neurologic features), the traditional therapeutic approach consists of a combination of prednisone and immunosuppressive agents (e.g., cyclophosphamide, azathioprine or mycophenolate), especially in patients with associated vasculitic involvement. However, some extraglandular features, such as interstitial nephritis, axonal polyneuropathy or ataxic neuronopathy, seem to have a poor response to corticosteroids and immunosuppressive agents.14