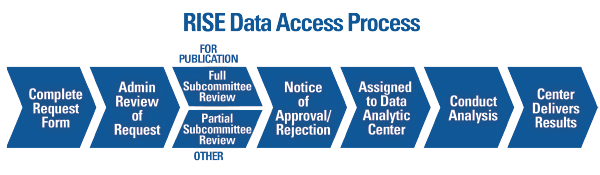
Figure 2. Overview of the process to request and complete a project using data from the Rheumatology Informatics System for Effectiveness (RISE) registry.
The process to review requests for use of RISE data can take two to three months, so if the data will be used for a grant-funded research project, the request should be completed early enough to allow for approval prior to the grant submission. To learn more about the process, visit the RISE for Research section of www.RISEregistry.org. Investigators are also encouraged to contact RISE staff directly at [email protected] to learn more about data that may be available through RISE for their research.
Note: The authors are an inter-professional rheumatology team that consists of four current/past members of the ARP Research Subcommittee, two RISE registry staff members and a member of the ACR Registries and Health Information Technology Committee.
References
- Francisco M, Johansson T, Kazi S. Overview of the American College of Rheumatology’s electronic health record-enabled registry: The Rheumatology Informatics System for Effectiveness. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2016 Sep–Oct;34(5 Suppl 101):S102–S104.
- Yazdany J, Bansback N, Clowse M, et al. Rheumatology Informatics System for Effectiveness: A national informatics-enabled registry for quality improvement. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2016 Dec;68(12):1866–1873.
- American College of Rheumatology. RISE for Practices. (n.d.).
- Yun H, Xie F, Chen L, et al. The effect of concomitant diabetes on RA-related outcomes: Results from the ACR’s RISE registry (abstract 223). Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(suppl 10).
- Schmajuk G, Evans M, Kay J, et al. Practice variation in prescriptions of non-TNFi biologics and tofacitinib: Data from the Rheumatology Informatics System for Effectiveness (RISE) registry (abstract 1887). Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(suppl 10).
- Yun H, Chen L, Xie F, et al. Do patients with moderate or high disease activity escalate ra therapy according to treat-to-target principles? Results from the ACR’s RISE registry (abstract 2856). Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(suppl 10).