Prolonged Time
In addition to using time as the qualifying factor for a higher E/M level, CPT also has face-to-face and non-face-to-face prolonged time codes that can be billed, in addition to an E/M code if time spent extends at least 30 minutes beyond the typical amount of time allotted for that visit. The CPT codes for face-to-face prolonged visits are 99354–99357, and these add-on codes cannot be billed separately without an E/M code.

CPT defines 99354 as “prolonged physician service in the office or other outpatient setting requiring direct (face-to-face) patient contact beyond the usual service; first hour.” For example, an established patient is seen with a level 5 office visit—typically 40 minutes long—but an extensive workup is performed due to multiple diagnoses, which requires the physician spend an extra 20 minutes with the patient. In this case, it is appropriate to code the claim as 99215 and 99354.
The non-face-to-face prolonged service codes without direct patient contact are 99358 and 99359. CPT allows codes 99358 and 99359 to be used when “a physician provides prolonged service not involving direct (face-to-face) care that is beyond the usual non–face-to-face component of physician service time.” These codes are to be reported in relation to other E/M services at any level, but may be reported for a different date of service than that of the primary E/M service they are related to.
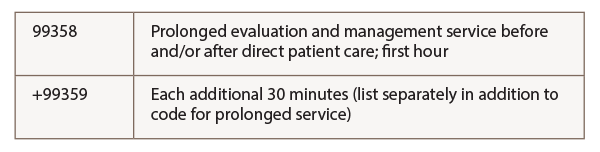
For example, if a physician spends an hour extensively reviewing a new patient’s medical records prior to their office visit, the time spent would be documented and included in the patient’s medical record during their scheduled visit. CPT codes 992XX and 99358 would be billed. For each additional 30 minutes over the first initial hour of the prolonged service, CPT code +99359 should be used. Note that 99359 is an add-on code and cannot be billed separately without 99358.
For more information on documenting the use of time, download a copy of the ACR’s Rheumatology Coding Manual, review the E/M services guidelines in the current CPT manual, or read Medicare’s Documentation Guidelines for E/M Services at www.cms.gov.
Time plays an important role in the selection of the most appropriate code for services. Understanding the rules related to time-based coding will help in obtaining proper payment as time is a key element necessary to help meet the appropriate treatment goals for patients. If you have any questions, contact Melesia Tillman CPC-I, CRCH, CHA, at [email protected] or 404-633-3777 x820.

