 EULAR 2022—Zoledronic acid is an injectable bisphosphonate approved for use in the U.S. to treat hypercalcemia of malignancy, multiple myeloma and patients with documented bone metastases from solid tumors in conjunction with standard antineoplastic therapy.1 Often, oral bisphosphonates, such as alendronate, ibandronate and risedronate, are used to treat osteoporosis.2 The use of bisphosphonates to treat osteoporosis has come under scrutiny due to reports of patients developing osteonecrosis of the jaw.
EULAR 2022—Zoledronic acid is an injectable bisphosphonate approved for use in the U.S. to treat hypercalcemia of malignancy, multiple myeloma and patients with documented bone metastases from solid tumors in conjunction with standard antineoplastic therapy.1 Often, oral bisphosphonates, such as alendronate, ibandronate and risedronate, are used to treat osteoporosis.2 The use of bisphosphonates to treat osteoporosis has come under scrutiny due to reports of patients developing osteonecrosis of the jaw.
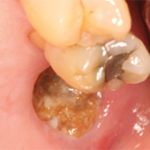
Claire Amigues from the Hospital Pasteur, Rheumatology, Nice, France, presented a study during EULAR 2022 that characterized zoledronate-related osteonecrosis of the jaw in patients with osteoporosis compared with the incidence of osteonecrosis of the jaw in patients treated with oral bisphosphonates.3,4
Methods
All reports of bisphosphonate adverse events from the French Pharmacovigilance Database from 1985 to 2020 were evaluated.3 For zoledronic acid, cases were separated by rheumatic or oncologic indications. For patients who developed osteonecrosis of the jaw, the potential risk factors analyzed included age, gender, smoking, having diabetes, having an alcohol use disorder, corticosteroid therapy, cancer, previous chemotherapy or immunotherapy, recent dental care and the time of bisphosphonate exposure.
Researchers assessed the association between the occurrence of osteonecrosis of the jaw and the bisphosphonate by calculating the reporting odds ratio in a case/non-case study. A stratification of assumed risk factors was performed to assess their effect on the patient risk of osteonecrosis of the jaw. The incidence of osteonecrosis of the jaw while receiving bisphosphonate therapy between 2011 and 2020 was estimated by relating the number of osteonecrosis of the jaw cases while receiving bisphosphonate therapy reported to the French Pharmacovigilance Database to the estimated number of patients treated with zoledronic acid, alendronate and risedronate over the same period according to health insurance reimbursement data. Incidence rate calculations, confidence interval calculations and comparison of incidence rates were performed.
Results
For patients treated with zoledronic acid, 2,254 adverse events were reported. Of these, 1,103 adverse events were reported in patients receiving zoledronic acid for oncologic indications, of which 568 cases were osteonecrosis of the jaw. For patients with rheumatologic indications receiving zoledronic acid, 1,151 adverse events were reported, of which 70 cases were osteonecrosis of the jaw.
In the patients with rheumatologic indications, 30 had recently undergone dental care and had a mean time of bisphosphonate exposure of 48.7 months. Risk factors for developing osteonecrosis of the jaw were smoking and a history of cancer and chemotherapy.