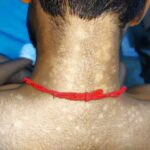
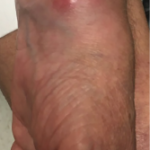
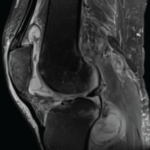
Autoimmune rheumatic diseases (AIRDs) are known for their systemic presentations and multi-organ involvement. Numerous infectious diseases, particularly mycobacterial, fungal and indolent bacterial infections endemic to specific geographic regions, present with varied signs and symptoms of multi-system involvement and can mimic AIRDs. Thus, differentiating infection from an AIRD is critical to resolve competing treatment approaches. This…