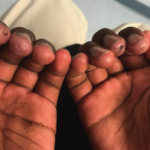
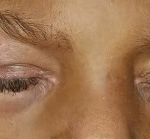
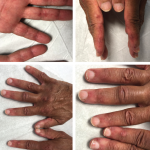
Juvenile dermatomyositis (JDM) is a childhood form of inflammatory myopathy affecting children younger than 18 years. The diagnosis of JDM is based on characteristic clinical features of proximal muscle weakness, skin rash, elevated muscle enzymes, magnetic resonance imaging and muscle biopsy.1 Autoantibodies seen in patients with inflammatory myopathy are not only associated with particular phenotypes…