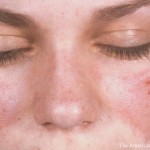
Could your lupus patients benefit from limiting exposure to chemicals at home and in the medical environment? It’s a strong possibility, according to the preliminary findings of a research team investigating DNA methylation disruption in patients with SLE…