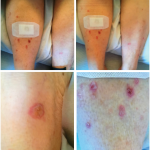
Image Credit: moomsabuy/shutterstock.com
SAN FRANCISCO—To help rheumatologists better understand the underlying mechanisms of autoimmune diseases, Mark Anderson, MD, PhD, professor of adult endocrinology, University of California, San Francisco, spoke during the 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting on ways in which immune regulation and tolerance work to ensure health in individuals who maintain tolerance to self-antigens and how these processes fail in those in whom autoimmune disease develops.
In his session, Immune Regulation and Tolerance, Dr. Anderson emphasized the key role of immune regulation for adaptive immunity that is characterized by a balancing act between activation effector T cells and tolerance T cells. He said that immune regulation is the way in which the body restrains its response to self antigens or external pathogens that get out of control.
Important to maintaining this balancing act requires controlling key switches that, when turned on inappropriately, can lead to pathogenic disease or autoimmune disease. “We now know that many of these switches have genetic underpinnings and are regulated by reactions to the environment,” said Dr. Anderson.
What We’re Learning from Cancer Immunology

Dr. Anderson
Research in cancer immunology, according to Dr. Anderson, is providing exciting insights into the therapeutic potential of either inhibiting or activating immunity to treat certain cancers.
He said that an active pathway in drug development is the programmed cell death (PD)-1 pathway. This pathway plays a role in cancer, as well as in chronic infection. He cited research showing T cell expansion in individuals with chronic viral infection, as well as data from mouse experiments showing that the PD-1 pathway helps shut down the response to viral infection to reduce collateral damage to tissue.1
Dr. Anderson also highlighted current investigation into the increasing recognized role that follicular helper T cells are thought to play in balancing the PD-1 pathway (also see “T Follicular Helper Cells,”).
All of this research is being used to develop new cancer drugs, such as ipilimumab, that activate the immune system by targeting CTLA-4, a protein receptor that, when blocked, can help activate T cells so they can attack tumors.
He cautioned, however, that the use of these types of drugs to treat disease by activating the immune system may also incur risks that may lead to autoimmune reactions and other collateral damage. “In the right context,” he said, “these drugs can promote autoimmune disease.” Thus, he emphasized the need to weigh the severity of potential adverse reactions against the benefits of treatment.
Regulatory T Cells
Another area of active investigation that Dr. Anderson briefly spoke on is immune tolerance and how it is maintained. Critical to understanding how immune tolerance works is to understand the properties of regulatory T cells (Tregs) and how these cells are regulated.