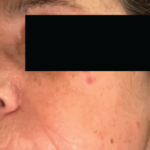
Patients with IgG4-RD have a predilection for forming mass lesions within organs. Thus, pseudotumors often lead to the patient’s clinical presentation and can lead to misdiagnoses of cancer. These are reported commonly in the orbital region, salivary glands, lung, kidney, lymph nodes, retroperitoneum, and other organs of patients with IgG4-RD.5 Many of these pseudotumors follow an indolent course, but local tissue destruction including erosion of bone has been reported.6 IgG4-RD can also cause more diffuse infiltrative lesions that involve the meninges, skin, or aorta. Aortic aneurysms and dissections can also occur, illustrative of the capacity of IgG4-RD to cause tissue-destructive lesions.5
Another feature of IgG4-RD is its association with allergic or atopic manifestations. Patients with IgG4-RD often have longstanding histories of allergic rhinitis, sinusitis, asthma, and other clinical features of this nature. Many patients have substantial elevations of serum IgE concentrations as well. Peripheral eosinophilia, sometimes on the order of 25% of the total white blood cell count, can be observed. As noted, mild to moderate eosinophil infiltration is also typical of tissue lesions.7
Specific Pathological Features of IgG4-RD
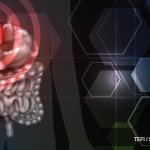
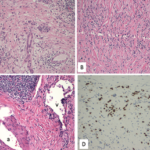
Organ involvement in IgG4-RD is characterized by a diffuse lymphoplasmocytic infiltration and an abundant presence of IgG4-positive plasma cells. Other features are storiform fibrosis, tumefactive lesions, obliterative phlebitis, and, as noted, a modest eosinophil infiltrate.8,9 The inflammatory infiltrate consists of B lymphocytes organized in germinal centers. Ample numbers of T cells are found throughout other parts of the affected tissue. Although IgG4-positive plasma cells are critical to the diagnosis, T cells comprise the dominant cell type in this disease.1
The finding of substantial numbers of IgG4-positive plasma cells in the involved tissue (and a high IgG4:total IgG ratio) is essential for the diagnosis of IgG4-RD. However, IgG4-positive plasma cells can be found in a wide variety of other inflammatory conditions as well and are by no means diagnostic of this condition.
The precise number of IgG4-positive plasma cells per high-power field required to provide strong evidence of the diagnosis of IgG4-RD varies somewhat according to the specific organ. A recent international consensus document provides guidance in this area.10 In salivary glands, for example, a minimum number of more than 100 IgG4-positive plasma cells are histologically highly suggestive of IgG4-RD.
In contrast, in a region such as the retroperitoneum, where the diagnosis of retroperitoneal fibrosis is usually not considered until the process of fibrosis is fairly advanced, there may be relatively few inflammatory cells of any type present. In such cases, the ratio of IgG4- to total IgG-bearing plasma cells may be more useful. In most tissues, a ratio greater than 0.50 strongly suggests the diagnosis of IgG4-RD.