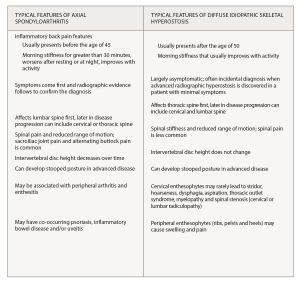
(click for larger image) Box 1*
* Information from Mader et al,1 Cuesta-Vargas et al.2 and Taurog et al.3
Isotretinoin, a vitamin A derivative, is commonly used for the treatment of severe recalcitrant acne vulgaris. Five biologically active forms of this compound are known, but only tretinoin and 4-oxo-tretinoin are recognized to bind to the retinoic acid receptor gamma (RAR-γ), leading to downstream improvement in acne. Although it is not directly antimicrobial, isotretinoin works to make the skin less habitable for Propionibacterium acnes and therefore reduces inflammation. It decreases the size of pilosebaceous ducts by targeting the smooth endoplasmic reticulum. This, in turn, decreases the amount of sebum produced.7
Prolonged courses and high doses of isotretinoin and other vitamin A derivatives have been linked to development of hyperostosis.8-10 The frequency of hyperostosis is unknown, but the U.S. Food and Drug Administration has observed “a high prevalence” among patients with disorders of keratinization when mean doses reached 2.24 mg/kg/day.11 When treating acne vulgaris, isotretinoin doses of 120 to 150 mg/kg are typically used as part of a 20-week course. However, in some cases, high cumulative doses (over 220 mg/kg) are used to reduce the risk of acne relapse.12
An excess of vitamin A has been associated with a range of bone pathologies. Case studies of individuals taking high doses of synthetic retinoids have demonstrated premature epiphyseal closure, increased cortical bone resorption and periosteal bone formation. These individuals endorsed skeletal and joint pain and exhibited hyperostosis in the long bones, metatarsals and metacarpals. Decreased bone mass, osteoporosis and fractures have been documented.6
It is hypothesized that isotretinoin contributes to hyperostosis through acceleration of skeletal maturation. Animal models have shown exposure to high levels of vitamin A lead to faster cartilage and periosteal growth and more bone remodeling.8 Although the mechanism of hyperostosis is unclear, two hypotheses could explain this phenomenon. One is that osteoblastic cells are stimulated by hypervitaminosis A, leading to more bone production.9 Another is that hypervitaminosis A leads to osteopenia, which then stimulates osteoblastic cells to produce more bone.9
Although it is uncertain whether vitamin A and its derivatives are involved in the development of DISH, some studies have found patients with DISH to have higher levels of vitamin A than the general population.1 Therefore, it is possible that DISH is a metabolic syndrome and that vitamin A plays a larger role in the manifestation of DISH than previously thought. Further studies are needed to understand the impact of high-dose retinoids on bone health and functional status.