At the time of the current hospital admission, the patient reported that she had gradually developed shortness of breath, subjective fevers and chills over the previous two months. Initially, she was evaluated at a local hospital where a computed tomography (CT) scan of the chest without contrast showed multifocal pulmonary infiltrates. Due to her symptoms (fevers, chills and shortness of breath), the patient was immediately started on intravenous antibiotics for possible multifocal pneumonia. She improved slightly, and the patient was discharged home to continue therapy with levofloxacin.
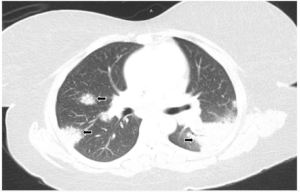
FIGURE 1A: Lung window from computed tomography pulmonary angiogram (CTPA) of the chest: Bilateral areas of pulmonary consolidation with air bronchograms (arrows).
At home, her clinical situation worsened significantly, and she presented in the emergency department at our hospital. This time, the patient was complaining about left-sided pleuritic chest pain and severe shortness of breath. Physical examination revealed a temperature of 98.4°F, respiratory rate of 18, heart rate of 84 and blood pressure of 127/64. The patient looked mildly distressed, had a nontender chest wall and, despite the CT findings, had clear lung fields. No skin rashes were identified.
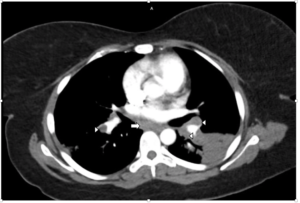
FIGURE 1B: Mediastinal window from CTPA showing bilateral hilar (arrowheads) and subcarinal (arrow) adenopathy. No evidence of pulmonary embolism was found (not shown).
The laboratory analysis demonstrated a white blood cell count of 10 k/mcL and a procalcitonin of <0.05 ng/mL. A CT pulmonary angiogram was requested and showed bilateral areas of pulmonary consolidation with air bronchograms, as well as bilateral hilar and subcarinal adenopathy (see Figures 1A and 1B). Despite the use of antibiotics, no improvement was noted.
We requested a consultation with a pulmonologist. Bronchoscopy showed no endobronchial lesions. Further, bronchial brushing cytology was negative for malignancy. A transbronchial biopsy of the pulmonary parenchyma was obtained and demonstrated non-necrotizing granulomas.
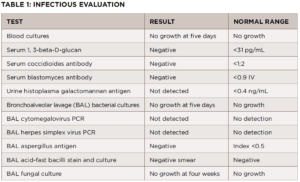
Further evaluation did not demonstrate evidence of a bacterial, viral or fungal infection (see Table 1). The antibiotic treatment was stopped. A follow-up chest X-ray was obtained four weeks later and showed no improvement in pulmonary infiltrates. A CT-guided core lung biopsy was performed to rule out cryptogenic organizing pneumonia; it again demonstrated non-necrotizing granulomas consistent with sarcoidosis (see Figure 2).
Reviewing the patient’s history, including the previous diagnoses (i.e., AOSD and RA) and prior treatments, we became concerned her condition might be a sarcoid-like reaction induced by a medication.