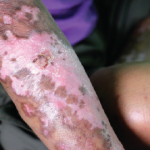
There are no drugs that are proven to help with calcinosis. Bisphosphonates have shown benefits in some studies but not in others. The antibiotic minocycline showed improvement in eight of nine limited cutaneous SSc patients at 50–100 mg a day. And the calcium-channel blocker Dilitiazem has been shown to be effective at high doses, but not low doses, Dr. Denton said.
TNF antagonists are a candidate, but that, too, is based on scant evidence. “There is a very limited amount of evidence to support the use of different treatments,” Dr. Denton said.
He stressed the importance of trials to understand the underlying genetics of calcinosis better and studies to get at associations and predictors that might lead to better interventions. He noted the start of the Scleroderma Clinical Trials Consortium and EULAR Scleroderma Trials and Research initiative to foster clinical trials on calcinosis in SSc. “This should be a research priority,” Dr. Denton said. “And certainly represents an unmet medical need.”
Thomas Collins is a freelance medical writer based in Florida.